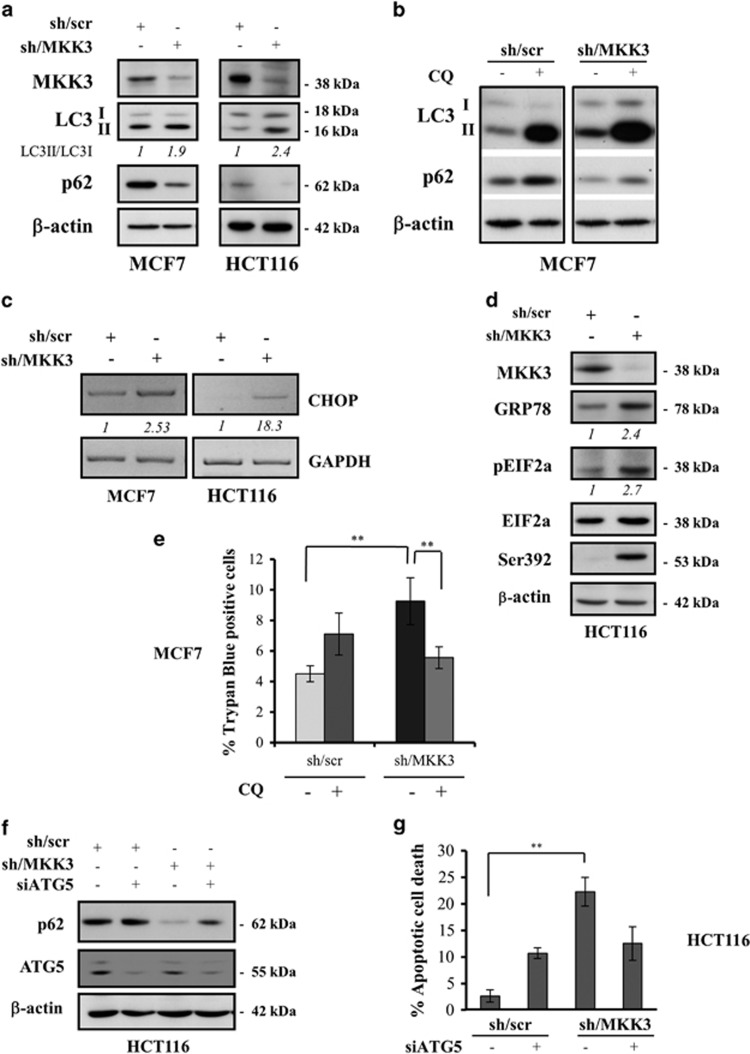
Figure 3.
MKK3 depletion induces autophagic cell death and ER stress in wtp53 cancer cells. Markers of autophagy LC3-I, LC3-II, and p62 upon MKK3 depletion were assessed by western blotting (a) in wtp53 MCF7 (left panel) and HCT116 (right panel) engineered -sh/scr and sh/MKK3 sublines. Seeded cells (1.5 × 105 cells/60 mm dish) were collected at 72 h post DOX delivery, and protein lysates (15 μg /lane) resolved in SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and probed with anti-MKK3-, anti-LC3-, and anti-SQSTM1/p62-specific antibodies. Densitometry analyses were performed with ImageJ software and LC3-II band intensity normalized to β-actin and quantified with respect to control tumors (sh/scr) set to 1.0. (b) MCF7-sh/scr and -sh/MKK3 sublines cultured in DOX condition (72 h) in the presence/absence of 25 μM CQ (48 h), then protein lysate were analyzed by western blot analysis with antibodies specific to LC3, SQSTM1/p62, and β actin (loading control). (c) Engineered sh/MKK3 and sh/scr MCF7 and HCT116 cultured 48 h with DOX were collected and total RNAs analyzed by RT-PCR with set of primers specific to CHOP and GAPDH (housekeeping gene). Densitometry was performed with the ImageJ software and relative CHOP mRNA levels were normalized to GAPDH and quantified with respect to control tumors (sh-scr) set to 1.0. (d) Engineered sh/scr and sh/MKK3 HCT116 cell lines were maintained in DOX condition for 36 h, then cells were collected and protein lysates (30 μg/lane) analyzed by western blot for the presence of ER stress proteins: phosphorylated EIF2A protein was evaluated using phospho-specific antibodies. Total amount of EIF2A was determined using anti-EIF2A antibody. GRP78/Bip was also used as marker of ER stress. Ser392 was analyzed as p53 stabilization marker. β-Actin was used as loading control. Densitometry was performed with the ImageJ software and relative ER stress marker protein levels were normalized to actin and quantified with respect to control tumors (sh-scr) set to 1.0. (e) Autophagy inhibition rescues the cell death induced by MKK3 depletion. Engineered MCF7-sh/scr and -sh/MKK3 sublines were seeded (1.5 × 105 cells/60 mm dish) in DOX condition for 24 h then treated/untreated with CQ (25 μM) and collected after 96 h of total DOX induction. Cell viability was evaluated with trypan blue exclusion assay. Results are reported as mean±S.D. of three independent experiments. Significance was assessed by Student's t-test, **P<0.01. (f) Engineered HCT116-sh/scr and -sh/MKK3 sublines were seeded (1.5 × 105 cells/60 mm dish) and maintained in DOX condition for 48 h, then transfected with siRNA for ATG5 (si-ATG5) or with control siRNA (si-ctr). Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were collected and protein lysates (15 μg/lane) resolved in SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-ATG5- and anti-SQSTM1/p62-specific antibodies. β-Actin was used as loading control. (g) Engineered HCT116-sh/scr and -sh/MKK3 sublines, treated as in f, were collected after 96 h of DOX induction and then stained with DAPI and ethidium bromide and analyzed by fluorescent microscope. The number of apoptotic dead cells was calculated and reported as a percentage of the total number of cell counted. Results are reported as means and S.D. of three independent experiments. **The significance (P<0.01) of death percent in sh/MKK3 with respect to sh/scr subline