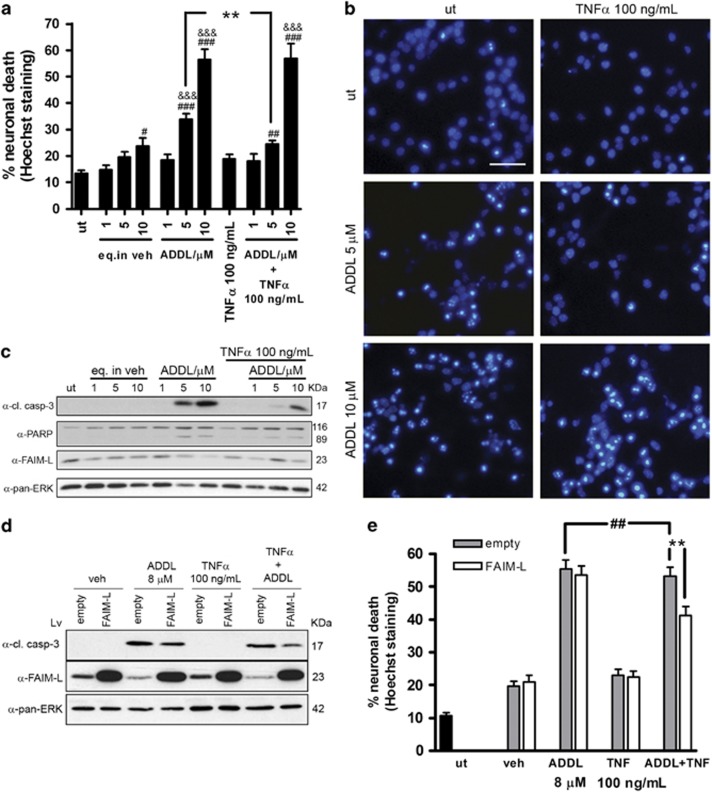
Figure 8.
The reduction of FAIM-L by Aβ impedes TNFα protection. (a) Cortical neuronal death determined by counting nuclei stained with Hoechst after 48 h of the indicated treatments. Data are mean±S.E.M. of three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA and Newman–Keuls post hoc. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01 and *P<0.05 (#versus untreated; &versus its vehicle; and * for comparisons between ADDLs and ADDLs+TNFα). (b) Representative images of nuclear Hoechst staining. Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) Immunoblot analysis of FAIM-L, PARP, and the cleavage fragment of caspase-3 in primary cortical neurons treated as in (a); pan-ERK was used as a control of loading. (d) Neurons were infected for the overexpression of FAIM-L or an empty lentivirus for 6 days and then treated for 48 h with 8 μM ADDLs and 100 ng/ml TNFα. Western blot analysis of caspase-3 cleavage and FAIM-L expression. Pan-ERK was used as a loading control. (e) Neurons were treated as in (d), and counts of nuclei after Hoechst staining were used to determine cell death. Graph represents mean±S.E.M. **, ##P<0.01 (*versus same treatment and #between ADDLs and ADDLs+TNFα). One-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparison Newman–Keuls test. In all cases, the experiments were repeated three times