Figure 3. Mean Escape Latency (in second), comparison among NM, Suc, Alc, SucTr, AlcTr, SucPWTr and AlcPWTr groups (n = 6-8).
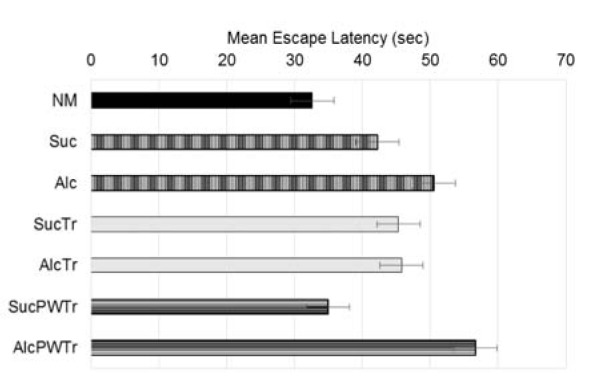
Data demonstrated as mean ± SEM. NM was able to escape within the shortest time (30.13 seconds). When compared among pair-fed groups, it was observed that offspring from AlcTr demonstrated similar time spent compared to pair-fed control (43.87 and 43.35 seconds, for AlcTr and SucTr, respectively). Offspring from Alc showed longer time spent to escape than Suc (48.84 and 40.17 seconds, for Alc and Suc, respectively). And AlcPWTr group also showed longer time spent to escape than pair-fed control (55.23 and 32.51 seconds, for AlcPWTr and SucPWTr, respectively). NM = normal control group; Alc = maternal alcohol treated group; Suc = Iso-caloric sucrose, pair-fed control group; AlcTr = Maternal alcohol + maternal taurine supplementation group; SucTr = Iso-caloric sucrose + maternal taurine supplementation, pair-fed control group; SucPWTr = Iso-caloric sucrose + post-wean offspring taurine supplementation, pair-fed control group; AlcPWTr = Maternal alcohol + post-wean offspring taurine supplementation group.
