FIGURE 3.
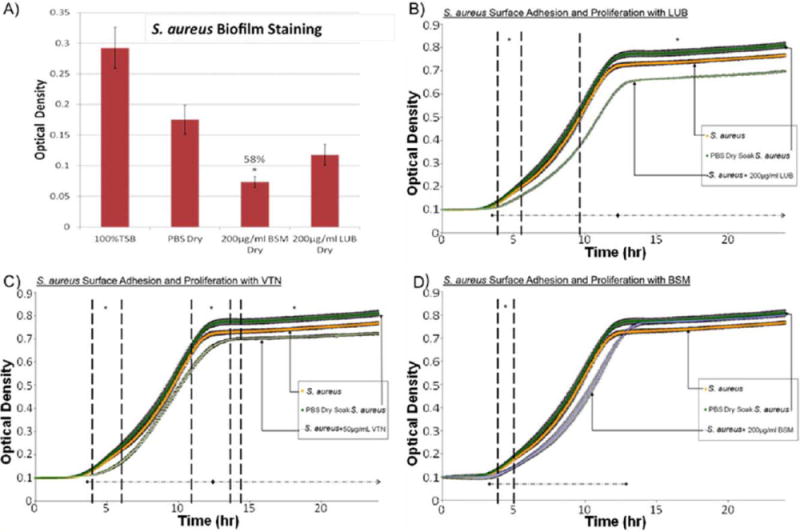
(A) Crystal violet results after a 24 h S. aureus surface adhesion and proliferation trial. BSM-treated samples showed significant reduction in biofilm formation. Approximately 58% less biofilm was measured on BSM coated samples versus PBS-treated samples. (B) S. aureus surface adhesion and proliferation with LUB (200 μg/mL) over 24 h determined by optical density readings. LUB treatment significantly suppressed bacterial growth over the course of 24 h by 13.9%. Data = mean ± SEM; N = 3 (at 24 h p < 0.01). (C) S. aureus surface adhesion and proliferation with VTN (50 μg/mL) over 24 h determined by optical density readings. VTN treatment significantly suppressed bacterial growth over the course of 24 hrs by 11%. Data = mean ± SEM; N = 3 (at 24 h p < 0.03). (D) S. aureus surface adhesion and proliferation with BSM (200 μg/mL) over 24 h determined by optical density readings. Some significant reduction in proliferation was seen between 4.2 and 4.9 h time points. Data = mean ± SEM; N = 3 [*indicates areas of significant difference between protein-treated trials and PBS-treated trials] as determined by p < 0.05; ◆ indicates areas where using a confidence interval of 95% a significance reduction was seen between protein-treated trials and PBS-treated trials]. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
