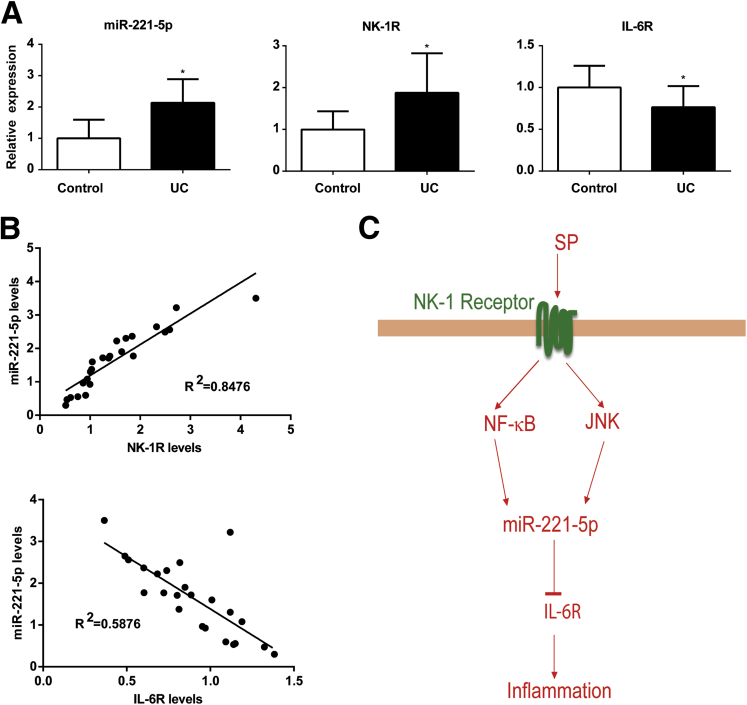
Figure 3.
Level of miR-221-5p in inflammatory bowel disease tissues. (A) Expression of microRNA (miR)-221-5p, neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R), and interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) in human ulcerative colitis (UC) tissue samples (n = 14) compared with control tissue samples (n = 10). *P < .05, data show mean ± standard deviation. (B) Correlation of miR-221-5p levels with NK-1R and IL-6R. The correlation coefficient was calculated using Prism6 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). (C) Schematic representation of proposed substance P (SP)–miRNA signaling pathway in human colonic epithelial cells. After binding with the NK-1R receptor, SP stimulates miR-221-5p expression via nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation in human colonic epithelial cells. MiR-221-5p regulates inflammation through down-regulation of IL-6R expression.