Fig 4. HbCIPK2 interacted with HbFd1.
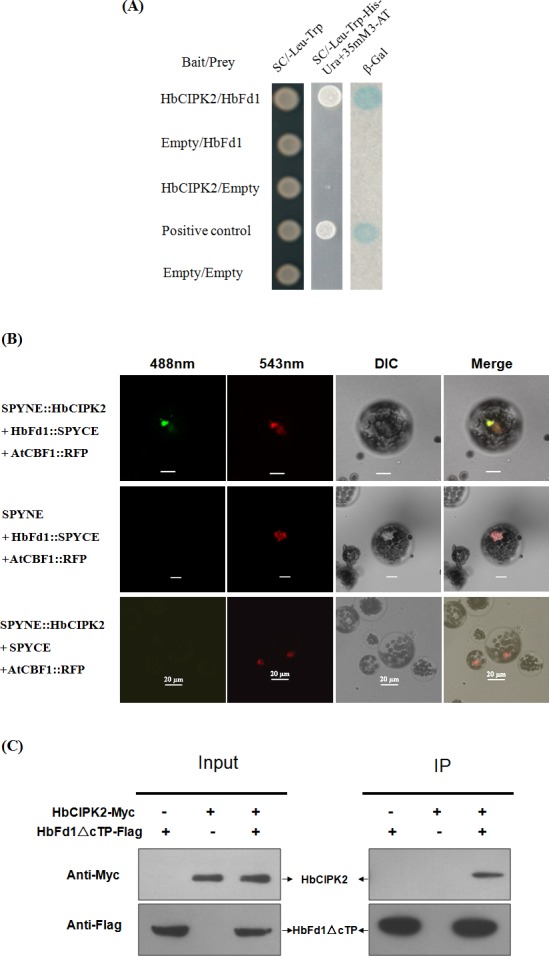
(A) Examination of the interaction between HbCIPK2 and HbFd1 in yeast. The interactions were verified by the yeast growing on selective medium (SC/-Leu-Trp-His-Ura with 35 mM 3-AT) and conducting ß-Gal assays. Bait vector with HbCIPK2 or prey vector with HbFd1 was transformed with empty vector as negative control, and the plasmids pPC97-Fos and pPC86-Jun provided by Invitrogen system were used as positive control. (B) Co-BiFC assay to verify the interaction of HbCIPK2 and HbFd1 in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Construct AtCBF1::RFP was used as reference to co-localize the interaction of HbFd1 with HbCIPK2, and transformants expressing SPYNE/HbFd1::SPYCE and SPYNE::HbCIPK2/SPYCE were used as negative controls. (C) Co-IP assay to show the interaction between HbCIPK2 and mature HbFd1 in cell line HEK293, co-expressing HbCIPK2-Myc and HbFd1△cTP-Flag. Cell proteins before (Input) and after (IP) immunoprecipitation were separated in SDS-PAGE gels, transferred onto the nitrocellulose membranes, and analyzed by protein gel blotting with antibodies as indicated. All assays repeated three times.
