Figure 1.
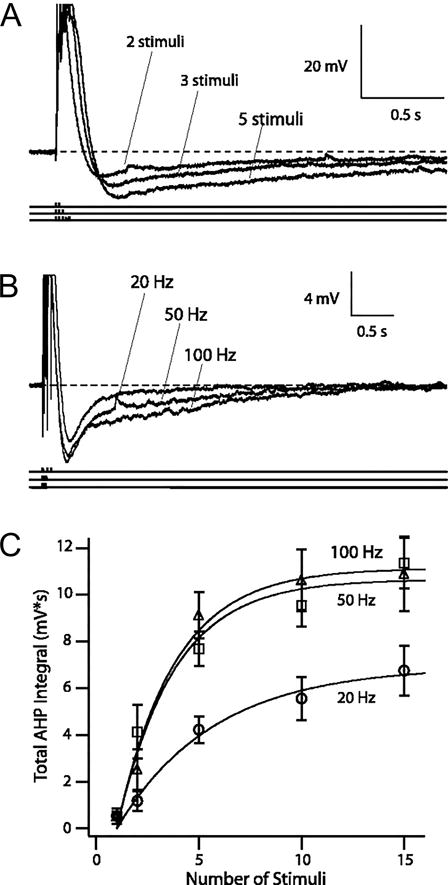
AHPs triggered by different patterns of suprathreshold synaptic stimuli. A: for a given stimulation frequency, AHP increased with each successive suprathreshold stimulus presentation. Representative voltage traces of AHPs triggered by 2, 3, and 5 suprathreshold stimuli at 50 Hz from a resting membrane potential of −68 mV. Action potentials were truncated for clarity. B: for a given number of stimuli, the AHP increased with increasing stimulation frequency. Representative voltage traces of AHPs evoked by 3 suprathreshold stimuli at 20, 50, and 100 Hz. C: frequency- and stimulus-dependence of AHP. Total AHP integral as a function of number of stimuli (1, 2, 5, 10, and 15) is plotted against stimulation frequencies (20 Hz, ○; 50 Hz, □; 100 Hz, ▵). Growths of AHP integrals were fit with monoexponential functions in the following form: Amax × (1 − exp{−[(no. stimuli − 1)/k]}), where Amax is the maximal total AHP integral, and k is the growth constant. Figure modified from Wu, Chan, and Disterhoft, J Neurophysiol. 2004, 92:2346–56.
