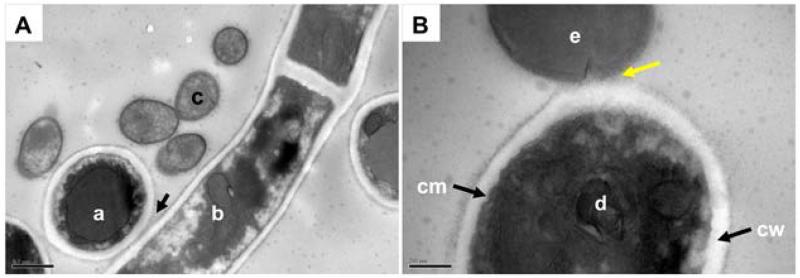
Fig. 2.
Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of C. albicans SC5314 cells interacting with S. gordonii DL1. Filamentation-induced C. albicans cells in YPT-Glc were incubated with S. gordonii cells for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were fixed, resin embedded and sectioned (see Experimental procedures) for visualization by TEM. Panel A, vertical cross section of a C. albicans hyphal filament (a) shows cell wall in close contact (arrowed) with the cell wall of a longitudinally-sectioned hyphal filament (b). Smaller streptococcal cells (c) can clearly be seen nearby expressing surface fibrillar structures. Panel B, shows the cell membrane (cm) and cell wall (cw) of a vertical section of a C. albicans hyphal filament (d) with the cell wall physically associated with the outer wall of an S. gordonii cell (e). The interaction is occurring at the newly forming septum of the streptococcal cell and the fibrils appear to interdigitate with the material on the C. albicans cell surface (yellow arrowed). Scale bars: A, 0.5 μm; B, 200 nm.