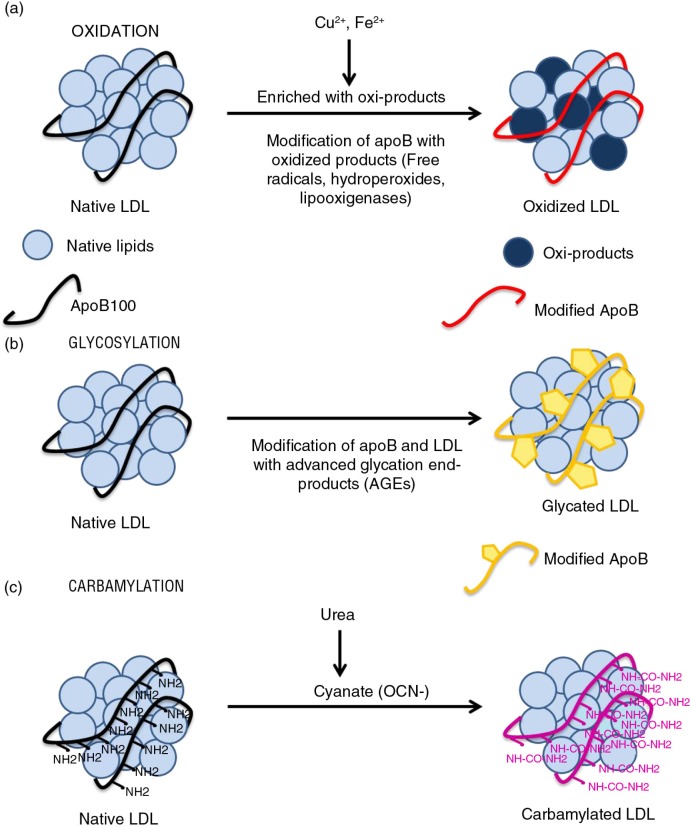
Fig. 1.
LDL modifications. (a) Oxidation: oxidized product-induced native LDL oxidation and modifications of apoB amino acids. (b) Glycosylation: modification of LDL and apoB by advanced glycosylation end-products (AGEs). (c) Carbamylation: cyanate from urea, which binds to NH2 groups in proteins – inducing their carbamylation – is generated by spontaneous dissociation from urea.