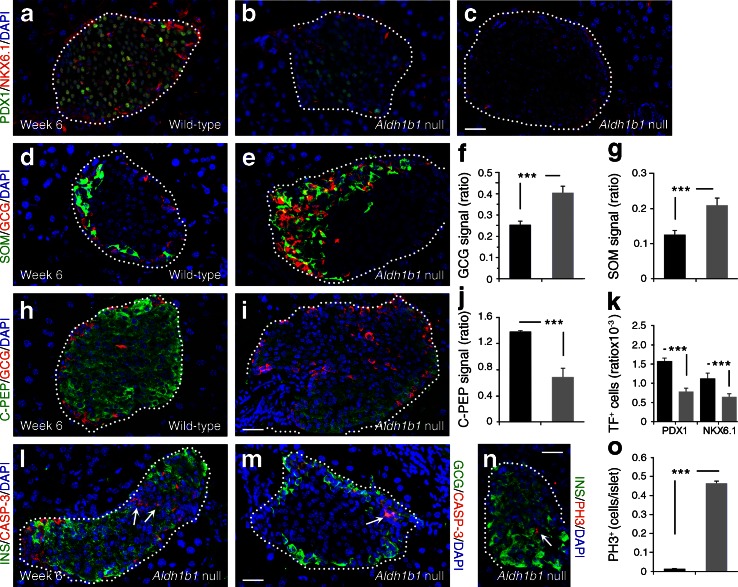
Fig. 3.
Islet patterning defects in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null young adult mouse islets. (a–c, h–i) Substantially lower (b) or absent (c) PDX1, NKX6.1 (a–c) and C-PEP (h, i) expression in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets. (d–g) Quantitative analysis of glucagon (GCG) and SOM (d, e) signal per islet (expressed as ratio of signal over DAPI signal) shows that the signal is increased by 60 and 65%, respectively (f, g), in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets (black bars, wild-type; grey bars, null). (j, k) Quantitative analysis of C-PEP signal (j) and PDX1+, NKX6.1+ cells (k) per islet (expressed as ratio of signal over DAPI signal) shows that their expression is significantly reduced in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets (black bars, wild-type; grey bars, null). (l, m) Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets showed increased levels of apoptosis as indicated by double immunofluorescence for caspase-3 (CASP-3) and either insulin (INS) (l) or GCG (m) (arrows). (n, o) Immunofluorescence for PH3 (n) indicated that mitotic activity was 50-fold higher (o) in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets (black bars, wild-type; grey bars, null). Results are from three to five animals per genotype, and values are representative of scoring at least 50 islets spanning the entire pancreas of each animal. Values are mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 for indicated comparisons. Scale bars, 25 μm (a–e, h, i, l–n). TF, transcription factor