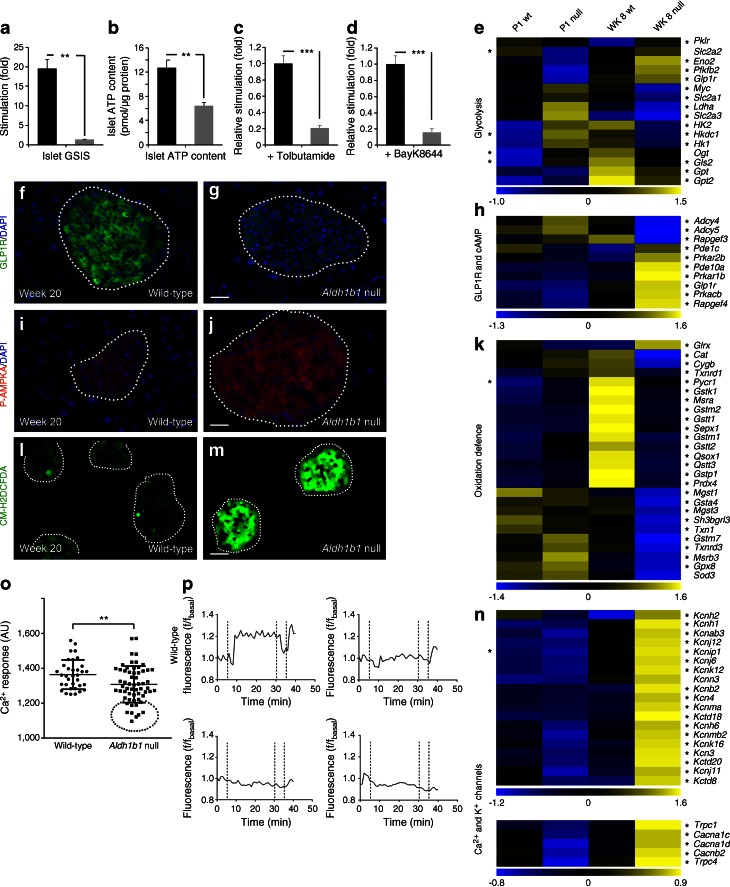
Fig. 5.
Glucose sensing and stimulus-coupling secretion are impaired in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null mice. (a, b) GSIS (a) and total ATP content (b) is reduced by 13-fold and twofold, respectively, in islets isolated from Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null mice compared with those isolated from wild-type mice (n = 3) (black bars, wild-type; grey bars, null). (c, d) Stimulation of insulin release in isolated islets with tolbutamide (c) or BayK8644 (d) is reduced by fivefold in the Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ nulls compared with those isolated from wild-type mice (n = 3) (black bars, wild-type; grey bars, null). (e–n) Immunofluorescence and gene expression analyses showed that Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets have dramatically reduced GLP1R expression (f, g), are energy depleted (i, j) and contain high levels of ROS (l, m). z score heat maps showed misregulated expression of several genes involved in glycolysis (e), GLP1R-mediated cAMP production (h) and oxidation defence (k), as well as Ca2+ and K+ channel genes (n) in the Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets. (o, p) Increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration, calculated as area under the curve in arbitrary units (AU), following glucose stimulation, is reduced in Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets (o). A subset of Aldh1b1 tm1lacZ null islets (circled in o) shows weak or absent intracellular Ca2+ mobilisation when compared with a typical wild-type response (wild-type response is shown in the upper left panel of p, the others represent affected islets). Horizontal lines in (o) represent the mean and SD; dotted lines in (p) represent injection time points of stimulation medium (5 min 20 s), baseline (35 min 20 s) and KCl (40 min 20 s). Results are from three to five animals per genotype. At least 25 islets per animal were scored or assayed. Values are means ± SEM. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 for indicated comparisons. Heat maps (e, h, k, n), *p adj ≤ 0.05: at the left side of the heat map * refers to comparisons at P1 whereas at the right side it refers to comparisons at WK 8. Scale bars, 25 μm (g, j) and 80 μm (m). WK, week; WT, wild-type