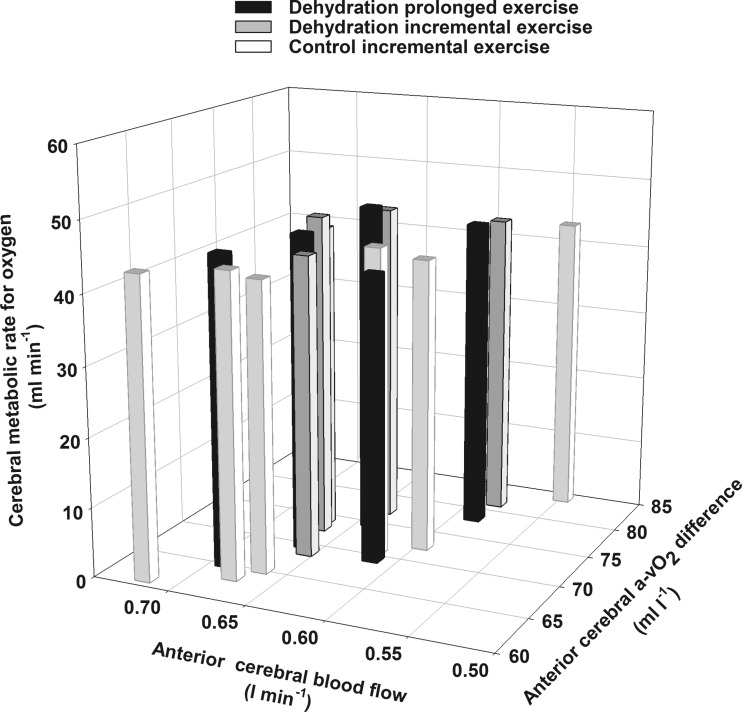
Fig. 6.
Anterior arterial to internal jugular venous O2 difference, anterior cerebral blood flow, and CMRO2 during prolonged and incremental exercise. Values are means ± SE during prolonged (n = 9) and incremental (n = 8) exercise. Baseline and incremental exercise to exhaustion data in control and dehydrated conditions have been previously reported (44). An inverse relationship between changes in blood flow and a-v O2 differences is shown (all points; R2 = −0.29, P = 0.01). Data are from a variety of exercise intensities, exercise durations, hydration status, and rest-to-exercise transitions where CMRO2 remained stable at ∼ 45 ml/min.