Figure 3.
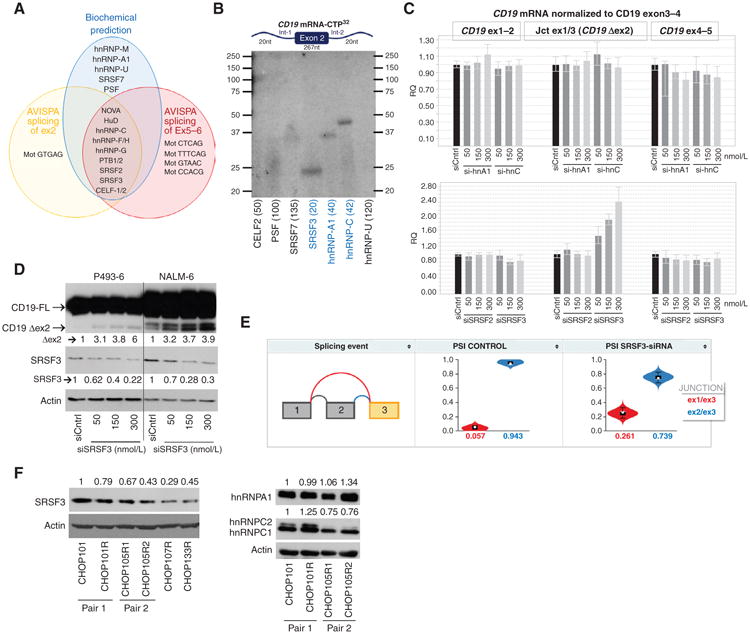
The splicing factor SRSF3 binds to and promotes inclusion of exon2 of CD19. A, Venn diagrams of splicing factors predicted by CD19 mRNA pull-down (biochemical predictions) or by the sequence-based algorithm AVISPA to bind to CD19 exon1–exon3 (splicing of exon2) or exon4–exon7 (splicing of exons 5–6) CD19 mRNA. B, RNA immunoprecipitation with antibodies against indicated proteins for detection of splicing factors that bind to mRNA CD19 exon2 and its flanking introns (not drawn to scale). Numbers in parentheses indicated expected molecular weights for each protein C, qRT-PCR analysis of CD19 Δex2 splicing variant in RNA from P493–6 transfected with increasing concentrations of si-hnRNPA1 or si-hRNPC (top graph) and siSRSF2 or siSRSF3 (bottom graph). D, immunoblotting for CD19 and SRSF3 in protein lysates from indicated cell lines transfected with increasing concentrations of siSRSF3 for 24 hours. Arrows indicate full-length (FL) and exon 2 skipping (Δex2) CD19 variants. Quantification of SRSF3 and Δex2 abundance relative to siRNA controls is shown. E, violin plots showing the distribution of PSI values (y-axis) quantified by MAJIQ for control (left) and SRSF3 knockdown (right) GM19238 B cells. Colors correspond to the junctions displayed in the thumbnail (far left) with the expected PSI value for each junction displayed on the x-axis. F, immunoblotting of SRSF3 (top) and hnRNPA1 and hnRNPC1/C2 (right) in xenografted tumor samples. Quantification of relative SRSF3, hnRNPA1, and hnRNPC protein abundance (numbers on left) was performed using Image J software (NIH).
