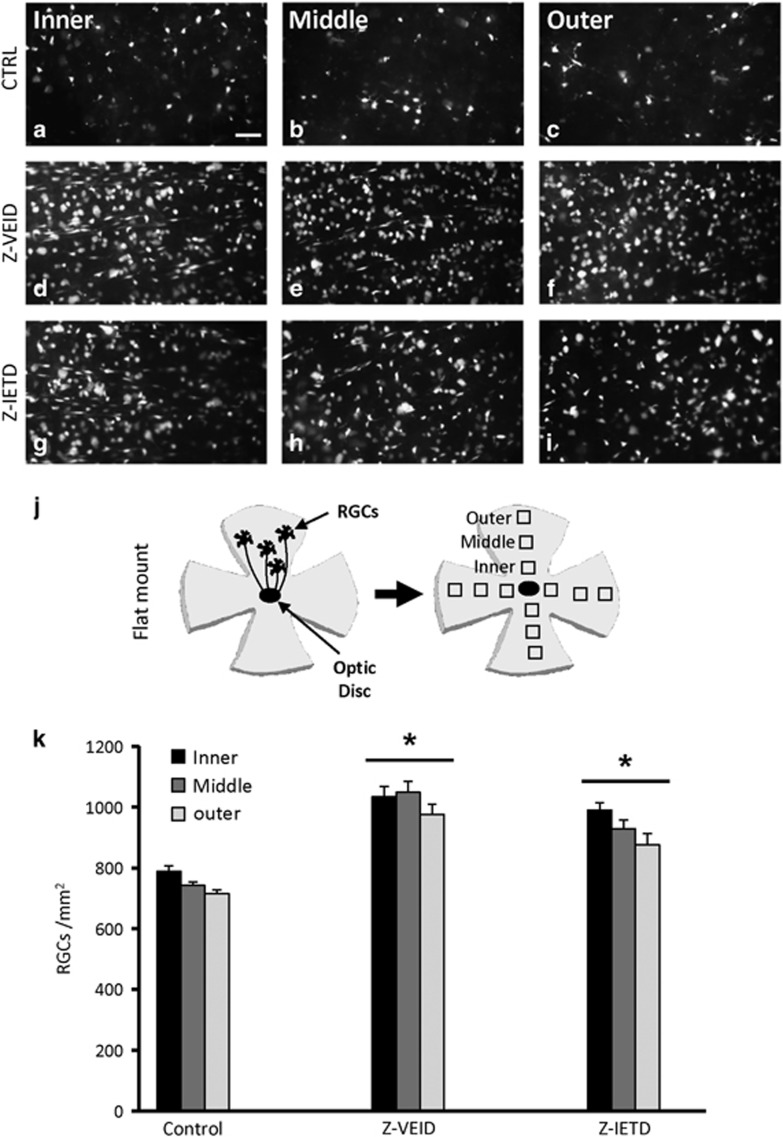
Figure 1.
Caspase inhibition promotes RGC survival after ophthalmic artery ligation. (a–i) Epifluorescence micrographs of flat-mounted retinas showing Fluorogold-labeled RGCs at 14 days following ophthalmic artery ligation and various treatments (a–c) control retinas (n=6) had few surviving RGCs; (d–f) caspase-6 inhibition (Z-VEID-FMK; n=6) and caspase-8 inhibition (Z-IETD-FMK; n=6; g–i) increased RGC survival after retinal ischemia; (j) schematic of retinal flat-mounts, showing the three eccentric areas of RGC quantification (inner, middle, outer); (k) quantification of the density (cells/mm2) of surviving RGCs (±S.E.M.) at 14 days following ophthalmic artery ligation and treatment with caspase inhibitors. Z-VEID (caspase-6 inhibitor) or Z-IETD (caspase-8 inhibitor) significantly increased RGC survival (*P<0.001) after retinal ischemia. Scale bar, 50 μm