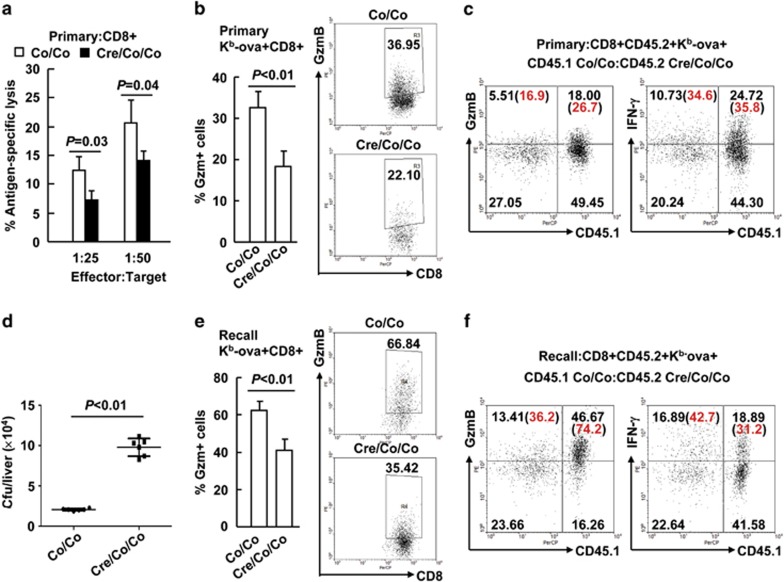
Figure 3.
Smad4 is required for the cytotoxic function of CD8+ T cells. (a and b) Six- to eight-week-old Smad4co/co;Lck-Cre mice and their littermate controls were infected with 5 × 103 c.f.u. of LM-OVA (n=6 per group). Single-cell suspensions from the spleen were prepared on day 7. (a) CD8+ cytotoxic activity was measured by specific killing of OVA peptide-loaded EL-4 cells. Peptide unloaded EL-4 cells were used as negative control. (b) GzmB expression in Kb-ova+CD8+ splenic T cells upon restimulation with the SIINFEKL peptide (10 nM, 6 h) was analyzed by intracellular staining and flow cytometry. (c) Bone marrow chimeric mice were prepared and treated as described in Figure 2d. The expression of CD45.1 and GzmB in Kb-ova+CD8+CD45.2+ splenic T cells at day 7 post infection upon OVA peptide restimulation was analyzed (n=3). (d and e) Smad4co/co;Lck-Cre mice and their littermates were rechallenged with 1 × 105 c.f.u. of LM-OVA 35 days after primary infection (n=6 per group). (d) Bacterial burden in the liver was determined 2 days after the secondary infection. (e) GzmB expression in Kb-ova+CD8+ splenic T cells upon OVA peptide restimulation was analyzed 5 days after the secondary infection. (f) Bone marrow chimeric mice were rechallenged with 1 × 105 c.f.u. of LM-OVA 35 days after primary infection. The expression of CD45.1 and GzmB in Kb-ova+CD8+CD45.2+ splenic T cells upon OVA peptide restimulation was analyzed 5 days after the secondary infection (n=3). Data shown in this figure are representative of at least three independent experiments