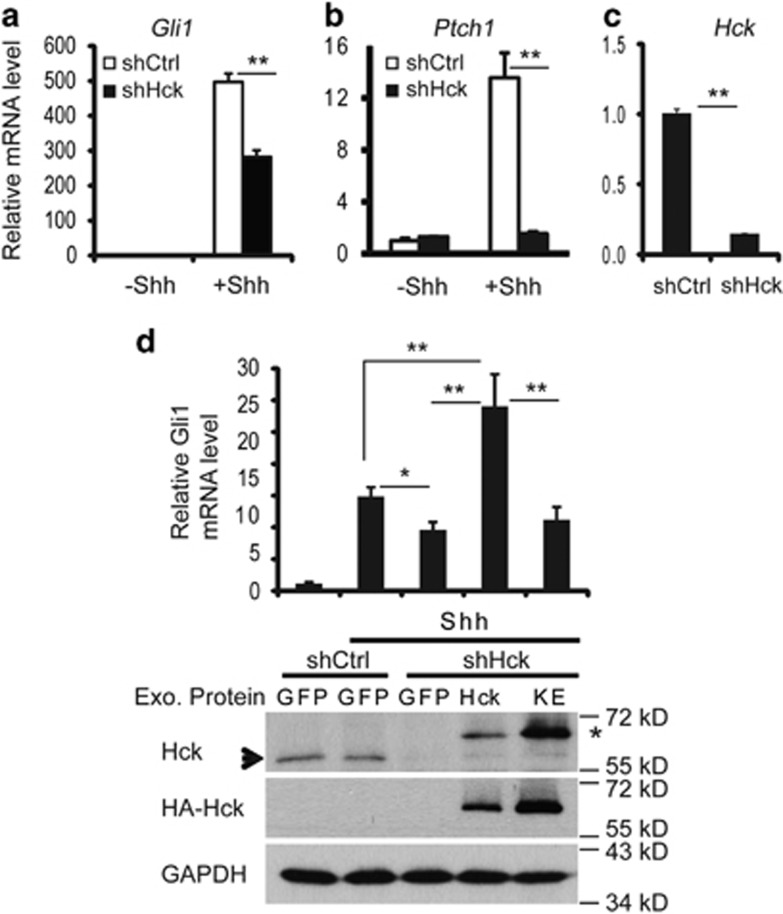
Figure 2.
Acute knockdown of Hck leads to impaired Shh signaling-induced gene expression. (a–c) NIH3T3 cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing scrambled shRNA (shCtrl) or shRNA designed to target Hck (shHck). The cells were treated with or without Shh-conditioned medium. mRNA levels of Shh target genes (a) Gli1, (b) Ptch1 and (c) Hck were determined by RT–qPCR. (d) NIH3T3 cells infected with lentiviruses expressing scrambled shRNA or shHck were co-infected with viruses for expression of Hck, Hck-K269E or GFP control. Upper panel: Endogenous Gli1 mRNA levels under basal or Shh-stimulated conditions were measured by RT–qPCR. Only wild-type Hck, but not the kinase-inactive Hck mutant (KE), rescued defective Shh-induced Gli1 expression that resulted from expression of shHck. Lower panel: western blot analyses of endogenous and exogenous Hck in samples analyzed by RT–PCR. An arrow points to the endogenous Hck band and a star indicates HA-Hck. Presented are means plus s.d.; n=3. Statistical analyses were performed using the Student's t-test; **P<0.01 and *P<0.05. qPCR, quantitative PCR.