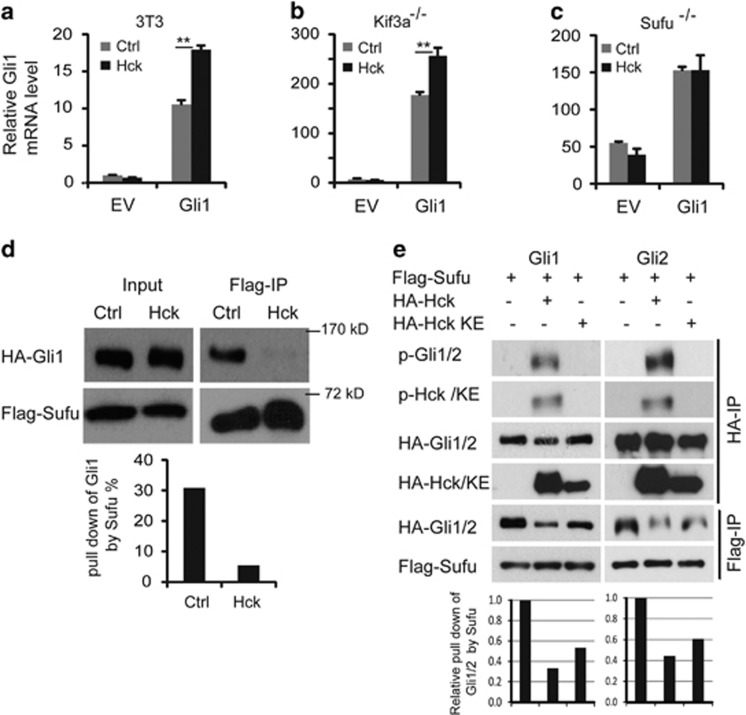
Figure 5.
Hck disrupts Gli–Sufu interactions. (a–c) Hck activates Gli1 downstream of Kif3a in a Sufu-dependent fashion. (a) NIH3T3 cells, (b) immortalized Kif3a−/− MEFs and (c) Sufu−/− MEFs were co-infected with a control or with lentiviruses designed to express Gli1 and/or Hck. Endogenous Gli1 levels measured using primers in the 5′-UTR were determined by RT–qPCR. Presented are means plus s.d.; n=3. Significance was determined by Student's t-test; **P<0.01. (d) Hck disrupts Gli1–Sufu interactions. NIH3T3 cells were transfected with constructs expressing HA-Gli1 and Flag-tagged Sufu in the presence or absence of exogenous HA-Hck. Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-Flag antibodies and western blotted with antibodies against HA or Flag. The western blot bands were quantified with NIH Image J software and the percentage of Gli1 precipitated with Flag-Sufu was compared with the input. (e) NIH3T3 cells were transfected with constructs expressing HA-Gli1/2 and Flag-Sufu in the presence of exogenous HA-Hck or kinase-inactive Hck-K269E. Cell lysates were precipitated with anti-Flag or anti-HA antibodies and western blotted with antibodies against HA, Flag or 4G10 antibodies. Quantifications of western blot are shown below. qPCR, quantitative PCR.