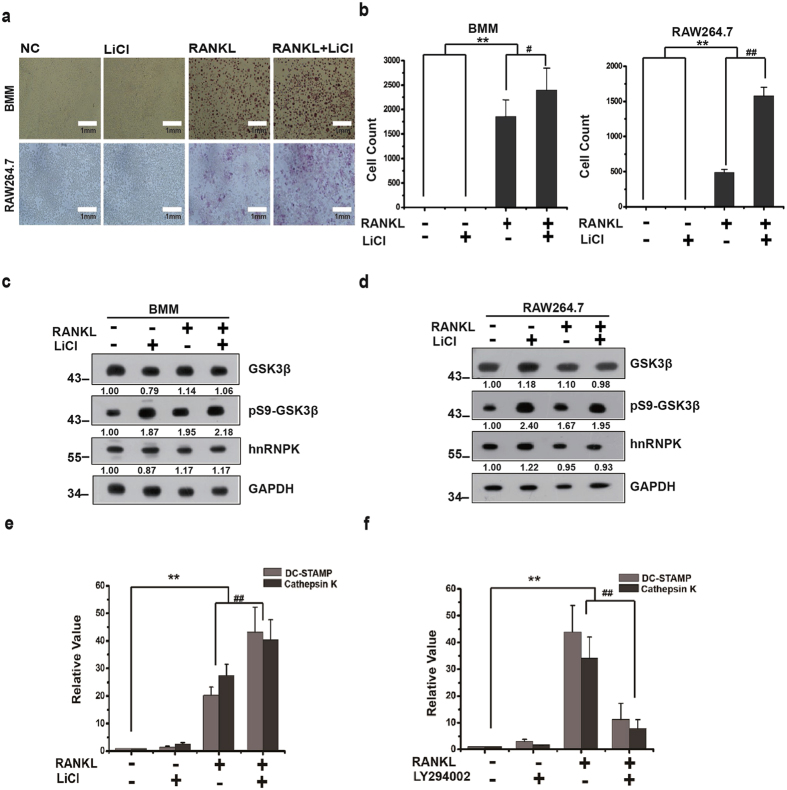
Figure 2. LiCl is unable to elicit the osteoclast differentiation but can enhance the effect of RANKL.
(a) Primary BMM or RAW264.7 cells were treated separately or jointly with LiCl and RANKL, then subjected to TRAP staining. Cells were photographed under microscope. Scale bars = 1 mm (b) Quantification of TRAP-positive cells. The mean values of TRAP-positive cells in 5 randomly chosen fields are presented. **/##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05. (c,d) Western blotting analysis of primary BMM or RAW264.7 cells treated as described in (a). The numbers under each protein band indicate the fold changes after normalization using GAPDH and in comparison with the control group. Gels were run under the same experimental conditions. For better clarity and conciseness of the presentation, cropped blots are shown. The raw uncropped images can be found in the Supplementary Figure 1. The cropping lines are indicated by black lines both in cropped and uncropped images. The results shown are representative of at least 3 experiments. (e,f) Total mRNA was extracted from RAW264.7 cells previously treated alone with RANKL, or in combination with either LiCl or LY294002, then reverse transcribed into cDNA. Real-time qPCR was subsequently performed for DC-STAMP and Cathepsin K expression. β-actin level was used for the normalization of the values. The results are presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments.