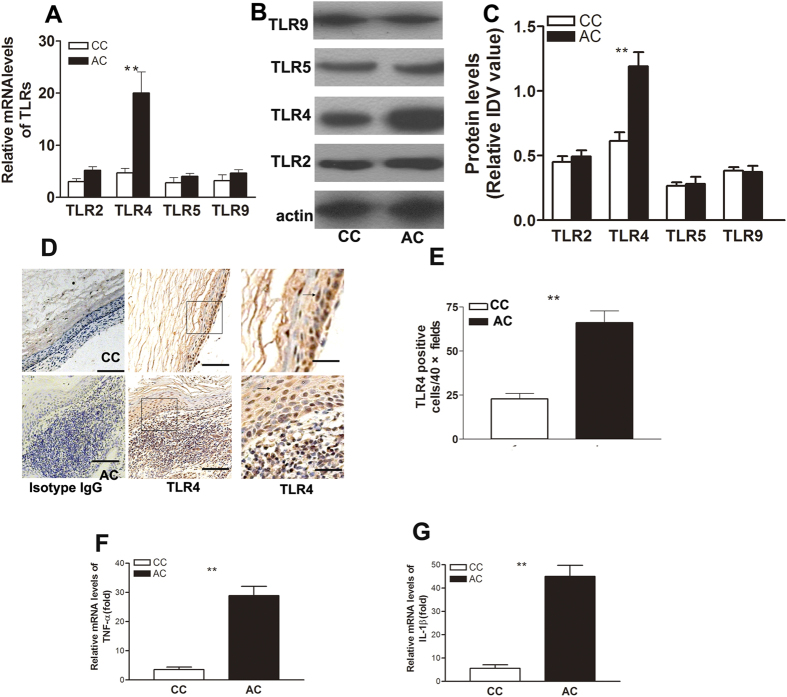
Figure 2. TLR4 and pro-inflammatory cytokines are up-regulated in human acquired cholesteatoma.
(A) TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, and TLR9 mRNA levels were measured in CC and AC patients using real-time PCR. The relative mRNA expression levels were calculated after normalization to those of β-actin. Data indicate the mean ± SEM of three individual experiments (n = 16 patients per experiment). The TLR4 mRNA transcript levels were significantly up-regulated in acquired cholesteatoma patients. (B) TLR protein levels were further examined using Western blotting. An equal amount of protein (20 μg) was loaded in each lane. Western blot data represent one of three individual experiments using 7–8 pooled mucosal samples/run, and individual experiments were carried out in triplicate (CC, n = 7; AC, n = 8). (C) Band intensity was quantitated and normalized to that of the β-actin control, TLR4 protein was the most increased in AC. (D–E) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining for TLR4 in CC and AC (n = 12).Lamellar sheets were keratin, and the brown cells were TLR4-positive.The number of TLR4-positive cells was much higher in AC. (F–G) The pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly up-regulated in AC compared with CC.Data represent the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments (n = 16 patients/experiment); CC: congenital cholesteatoma; AC: acquired cholesteatoma; **indicates P < 0.01.