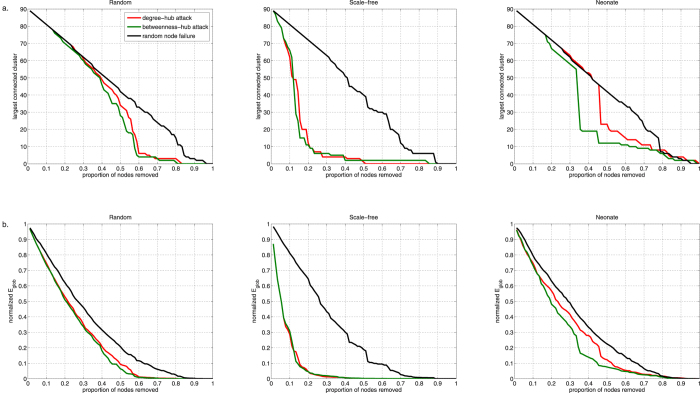
Figure 6. Resilience of resting state networks.
Response to targeted removal of degree (red) and betweenness (green) hubs and random removal of nodes (black) are shown for neonate and comparable random and scale-free networks. The effects of node removal to the largest connected cluster (A) and global efficiency (B) of the network are shown. The neonate brain is more resilient to targeted attack of hubs compared to a scale-free network. Attack on betweenness hubs in the neonate brain decreases global efficiency and the size of the largest cluster faster than attack on degree hubs.