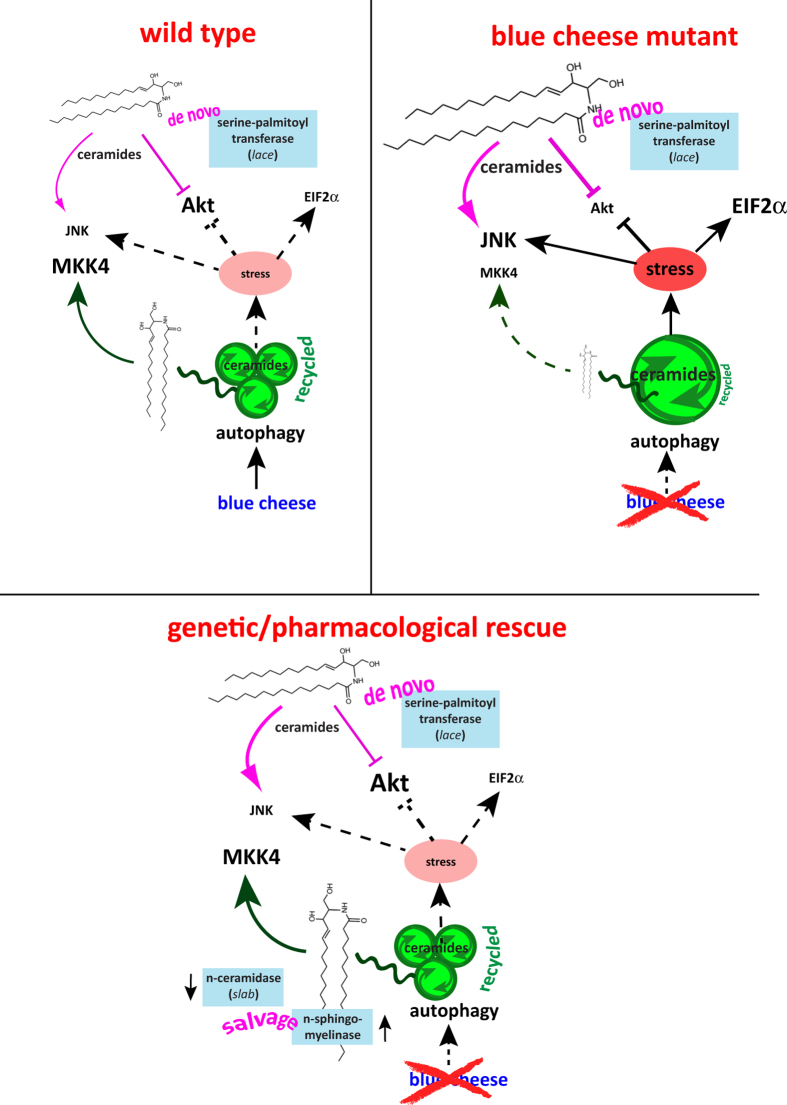
Figure 8. Model summarizing key sphingolipid metabolic pathways contributing to de novo (pink) and salvaged ceramide pools (green), whose normal balance (‘wild type’ situation) may be perturbed by bchs’ blockage of normal autophagic clearance (‘blue cheese mutant’), which increases stress and impinges on survival pathways involving MKK4, JNK, Akt, and EIF2α.
Rescue of these signaling pathways, and of neuronal death (‘genetic/pharmacological rescue’), can be achieved by genetic increases in salvage pathways, or by increases in autophagic clearance. Suppression of de novo synthesis via spt (lace) reduction or treatment with pharmacological agents, only partially rescues signaling pathways (JNK and Akt) but does not rescue neuronal death.