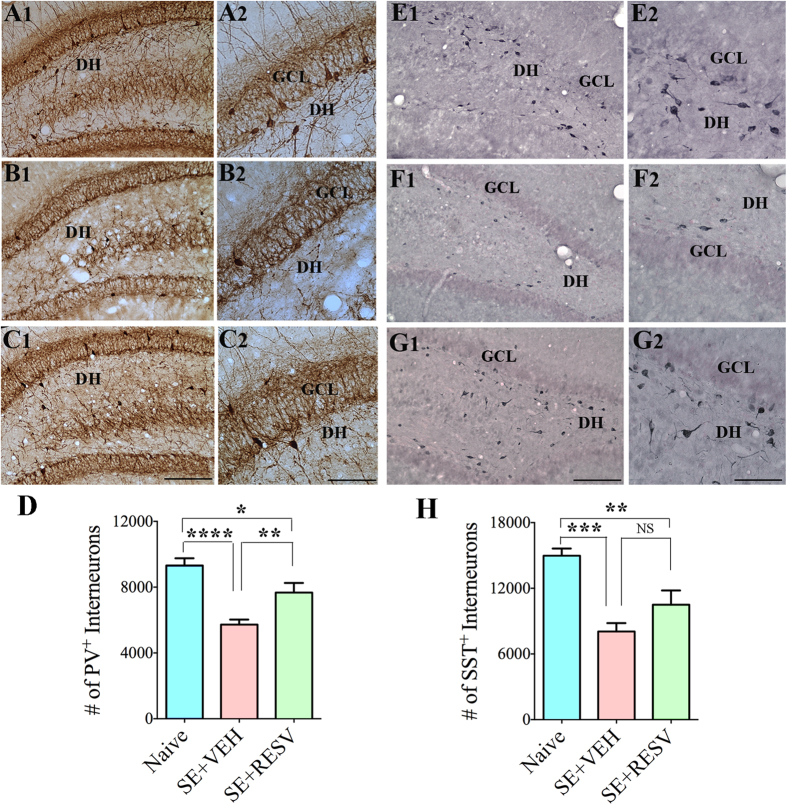
Figure 3. Resveratrol (RESV) treatment after status epilepticus (SE) lowered the loss of interneurons expressing parvalbumin (PV) and somatostatin (SST) in the dentate gyrus (DG).
Figures A1, B1 and C1 show the distribution of PV + interneurons in the DG from a naïve control rat (A1) and rats that received vehicle (VEH; B1) or RESV (C1) after SE. Figures A2, B2 and C2 are magnified views of regions from A1, B1 and C1. Figures E1, F1 and G1 show the distribution of SST + interneurons in the DG from a naïve control rat (E1) and rats that received VEH (F1) or RESV (C1) after SE. Figures E2, F2 and G2 are magnified views of regions from E1, F1 and G1. DH, Dentate hilus; GCL, granule cell layer. Scale bar: A1, B1, C1, E1, F1 and G1, 200 μm; A2, B2, C2, E2, F2 and G2, 100 μm. Bar charts compare numbers of interneurons positive for PV (D) and SST (H) in the DG between naïve control rats and rats that received VEH or RESV after SE. Note that, in comparison to naïve control rats, rats receiving VEH after SE display considerable reductions in numbers of PV + and SST + interneurons. In contrast, rats receiving RESV during and after SE display moderate loss of PV + and SST + interneuron numbers and hence exhibit greater numbers surviving PV + and SST + interneurons than rats receiving VEH after SE. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.