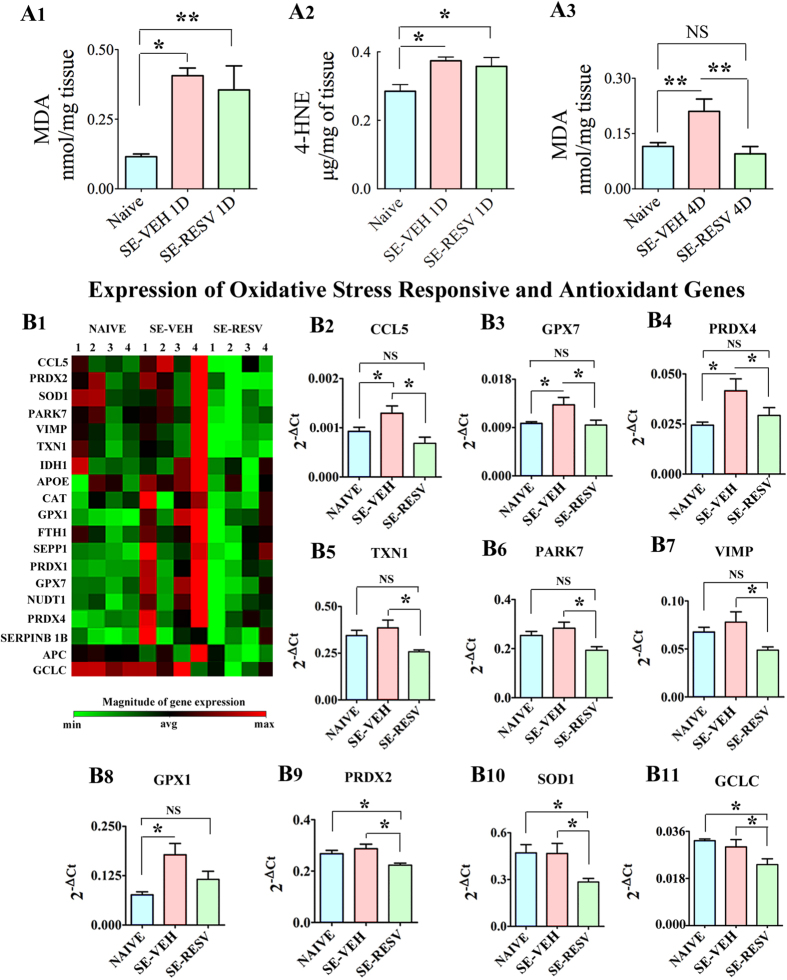
Figure 6. Resveratrol (RESV) treatment for 4 days normalized status epilepticus (SE) induced increased oxidative stress in the hippocampus.
Bar charts in A1, A2 and A3 compare concentrations of malondialdehyde (MDA; A1,A3) and 4-hydroxynoneal (4-HNE; A2) between different groups. When measured a day after SE, rats receiving vehicle (VEH) or RESV showed increased concentration of MDA (A1) and 4-HNE (A2) in comparison to naive control rats. However, when measured 4 days after SE, MDA concentration was normalized to control levels in rats receiving RESV but remained upregulated in rats receiving VEH after SE (A3), implying the beneficial effects of RESV treatment for 4 days after SE. Figure B1 illustrates the expression (heat map) of select oxidative stress responsive and antioxidant genes measured through quantitative real time PCR array in the hippocampus. Note that, in comparison to their expression in naive control rats, many genes show a trend towards increased expression in rats receiving VEH after SE but normalized expression in rats receiving RESV during and after SE (B1), suggesting extinction of increased oxidative stress with RESV treatment. Bar charts in B2-B11 compare the expression of specific genes between the three groups. Note that, RESV treatment after SE normalized the expression of genes CCL5, GPX7, PRDX4, TXN1, PARK7, VIMP and GPX1 to control levels (B2–B8) and lowered the expression of genes PRDX2, SOD1 and GCLC to below control levels (B9–B11), implying considerable moderation of oxidative stress in the hippocampus by RESV treatment.