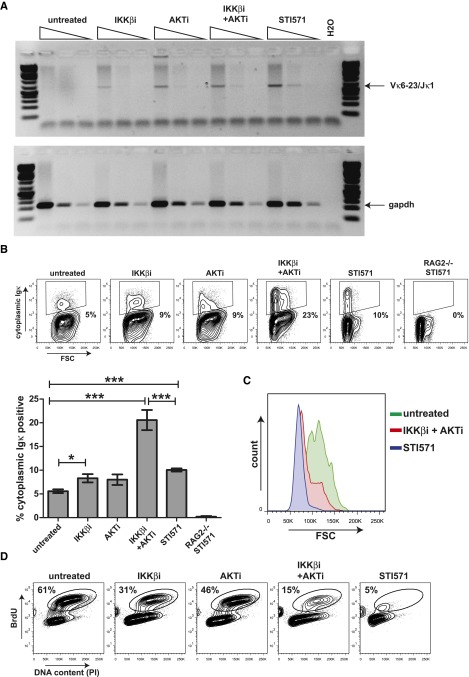
Figure 3.
Inhibition of AKT and NF-κB signaling results in recombination of the endogenous Iglκ locus in mouse Abl pre-B cells. (A) Semiquantitative PCR analysis of Vκ6-23 to Jκ1 coding joins in mouse Abl pre-B cells treated with 2.5 μM IKKβi, 2.5 μM AKTi, or 10 μM STI571 for 72 hours. Semiquantitative PCR analysis for Gapdh was performed as a loading control. (B) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) plots showing cytoplasmic Igκ expression vs forward scatter (FSC) in mouse Abl pre-B cells stimulated as in (A). Numbers below outlined gates indicate percentage of cells. Graph depicts percentages of cytoplasmic Igκ-positive cells in mouse Abl pre-B cell cultures stimulated for 72 hours. A representative example of 2 independent experiments is shown, 4 replicate measurements were performed per experiment, and error bars represent means ± SD. Statistical significances between groups were determined by 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using a Bonferroni’s posttest. (C) Representative FACS plot showing overlay FSC histograms of cytoplasmic Igκ-positive mouse Abl pre-B cells treated as indicated. (D) Representative FACS plots showing BrdU incorporation vs DNA content as measured by propidium iodide (PI) staining in mouse Abl pre-B cells treated for 48 hours as indicated above FACS plots. Numbers above outlined gates indicate percentage of cells. *P < .05; ***P < .001.