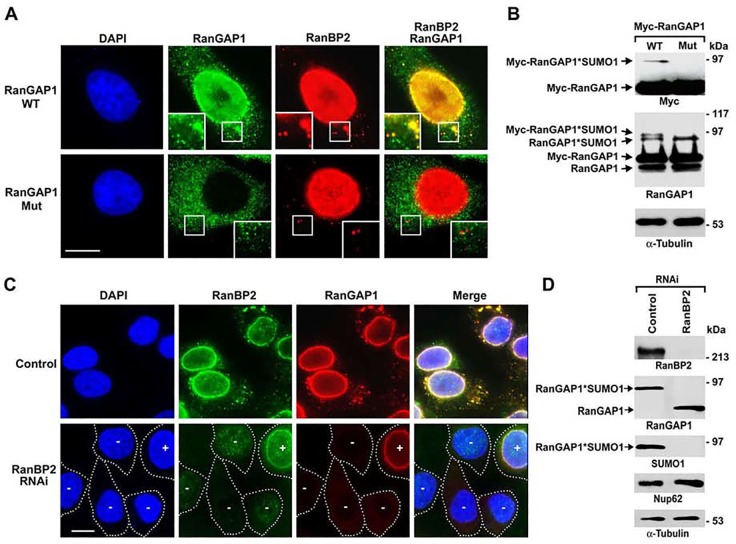
Fig 3. Both covalent SUMOylation and non-covalent interaction with RanBP2 are required for RanGAP1 localization to ALPCs.
(A) HeLa cells were transfected with the constructs encoding Myc-tagged RanGAP1 wild-type (WT) or SUMOylation-deficient K526R mutant (Mut) and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy with antibodies specific to Myc and RanBP2. The boxes at the bottom corner of each image show the enlarged version of inlets. Bar, 10 μm. (B) The transfected cells were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific to RanGAP1, Myc and α-tubulin. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with control or RanBP2-specific siRNAs, double-stained with antibodies specific to RanBP2 and RanGAP1, and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy. In the lower panel, white dashed lines indicate the borders of RanBP2 RNAi cells, in which “-” indicates a significant knockdown of RanBP2 and “+” indicates that the signals of RanBP2 are comparable to those in control RNAi cells (upper panel). Bar, 10 μm. (D) The cells transfected with control or RanBP2-specific siRNAs were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.