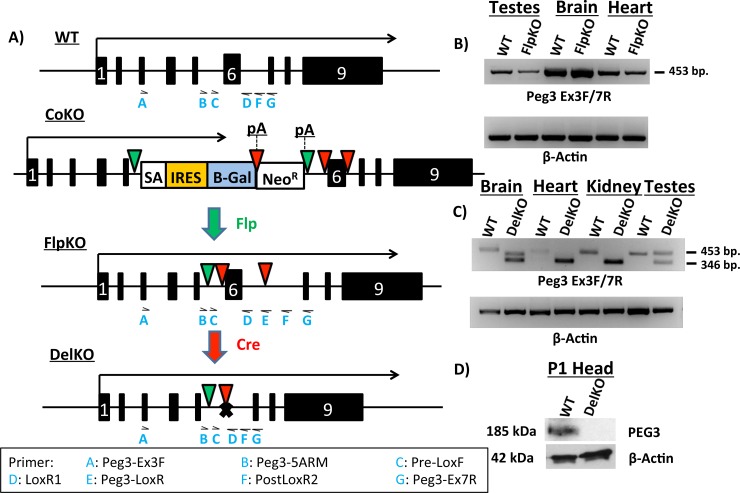
Fig 1. Molecular characterization of Peg3 FlpKO and Peg3 DelKO mouse lines.
(a) Schematic representation of Peg3 alleles. Arrows above each allele indicate transcriptional direction and length. Exons are indicated by boxes, with Exon 6 denoted as a white “6”. Flippase recognition target (FRT) sites are shown as green triangles. LoxP sites are indicated by red triangles. In the Peg3 CoKO allele, we inserted a cassette containing a splice acceptor (SA) sequence, an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) and a β-Galactosidase (β-Gal) reporter gene, followed by a poly-adenylation signal (pA). Neomycin Resistance gene (NeoR) is followed by another pA. Crossing Peg3 CoKO mice with a Flp-expressing line results in the Peg3 FlpKO allele. Successive crossing of Peg3 FlpKO mice with Cre-expressing lines results in the Peg3 DelKO allele. (b) RT-PCR of Peg3 from various tissues in Peg3 FlpKO line. β-Actin was used as an internal control. (c) RT-PCR of Peg3 from various tissues in Peg3 DelKO. Cre-mediated recombination of Exon 6 results in the smaller amplicon size (346 bp in length) as compared to the wild-type product (453 bp in length). (d) Western blots from the 1-day-old heads of Peg3 DelKO. To visualize expression of PEG3 protein, western blots were probed for Peg3, stripped and then probed for β-Actin. Locations of primers used in this study are indicated as blue letters under each allele. The Primer legend at the bottom shows which primer corresponds to each abbreviation.