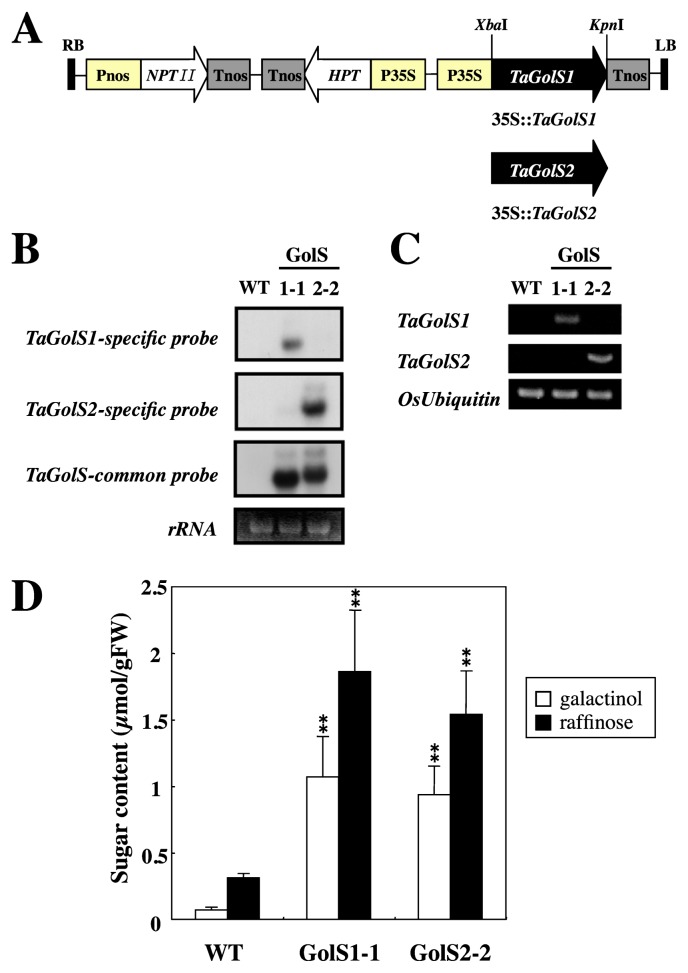
Fig. 3.
Analysis of transgenic rice lines overexpressing TaGolS. A. Schematic representation of the construct used to overexpress TaGolS1 or TaGolS2 in rice. Pnos, promoter sequence of nopaline synthase gene; NPTII, neomycine phosphotransferase gene; Tnos, terminator sequence of nopaline synthase gene; HPT, hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene; P35S, promoter sequence of the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV)35S; TaGolS1 and TaGolS2, galactinol synthase cDNA from wheat; RB, right T-DNA border; LB, left T-DNA border. B. Expression of TaGolS1 and TaGolS2 in transgenic rice lines (T1 generation) determined by Northern analysis. Ethidium bromide-stained rRNA bands are shown at the bottom. C. Specific expression of TaGolS1 and TaGolS2 in transgenic rice lines (T1 generation) determined by RT-PCR analysis. D. Galactinol and raffinose contents of transgenic rice lines overexpressing TaGolS1 or TaGolS2. Mature leaves were sampled from wild-type (WT) and two independent transgenic lines (GolS 1-1 and GolS 2-2: T1 generation). Each data point represents the mean ± standard deviation from four individual plants. Bars labeled with asterisks show significant differences between WT and transgenic plants by Welch’s t-test at ** P = 0.01.