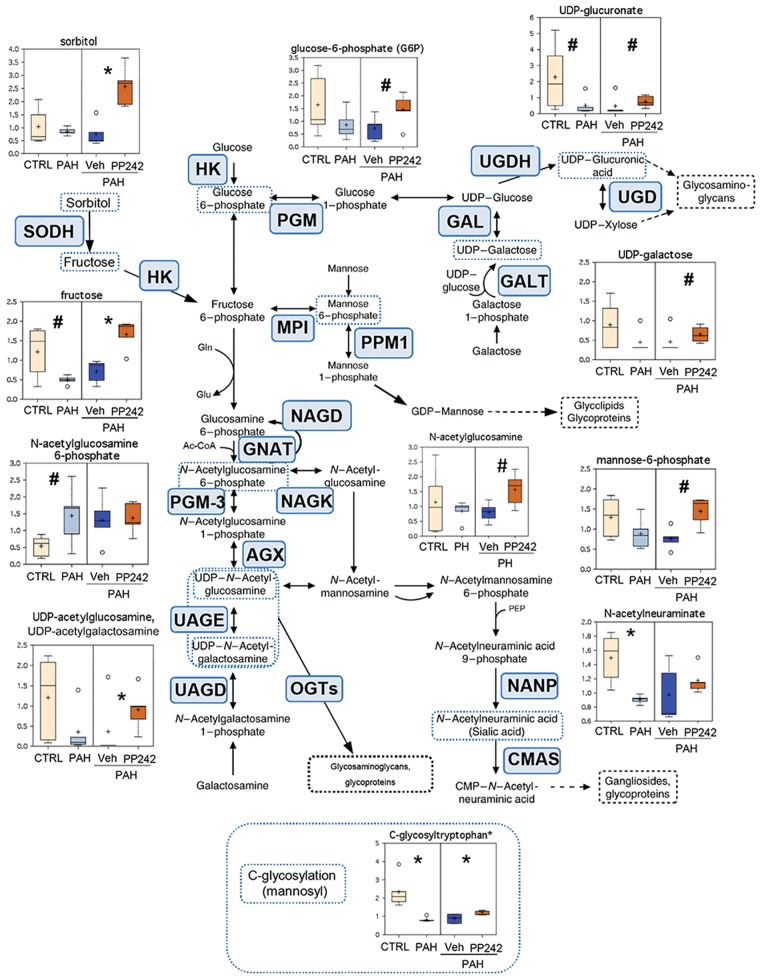
Figure 3.
Intermediates of carbohydrate metabolism and glycosylation pathways in control (CTRL), pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) pulmonary arterial vascular smooth muscle cells (PAVSMCs), and mTOR inhibitor PP242- and vehicle-treated PAH PAVSMCs. Box plots for the metabolites involved in glycosylation metabolism, combined with the reaction scheme including key components and enzymes, are shown. The metabolite data are presented as box-and-whiskers graphs as follows: light yellow: nondiseased (control) PAVSMCs; light blue: PAH PAVSMCs; dark blue: vehicle-treated PAH PAVSMCs (Veh); orange: PP242-treated PAH PAVSMCs (details in Fig. S2). Data are in arbitrary units normalized by protein concentration from 5 subjects/group; *P ≤ 0.05, #0.05 < P < 0.1 by the Welch 2-sample t test. Enzymes that catalyze particular steps in the pathway are shown in blue boxes labeled with their abbreviations according to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes database. AGX: UDP-N-acetylhexosamine pyrophosphorylase 1; CMAS: N-acylneuraminate cytidylyltransferase; GALE: UDP-glucose epimerase; GALT: UDP-glucose:alpha-D-galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase; GNAT: glucosamine-6-phosphate-acetyl transferase; HK: hexokinase; MPI: mannose-6-phosphate isomerase; NAGD: N-acetyl-glucosamine 6-phosphate deacetylase; NAGK: N-acetyl-glucosamine kinase; NANP: N-acylneuraminate-9-phosphatase; OGTs: O-GLCNAc transferases; PGM: phosphoglucomutase; PGM-3: phosphoglucomutase 3; PPM1: phosphomannomutase 1; SODH: sorbitol dehydrogenase; UAGD: UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine diphosphorylase; UAGE: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase; UGD: UDP-glucuronate decarboxylase; UGDH: UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase. Ac-CoA: acetyl coenzyme A; CMP: cytidine monophosphate; Gln: glutamine; Glu: glutamic acid; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; UDP: uridine diphosphate.