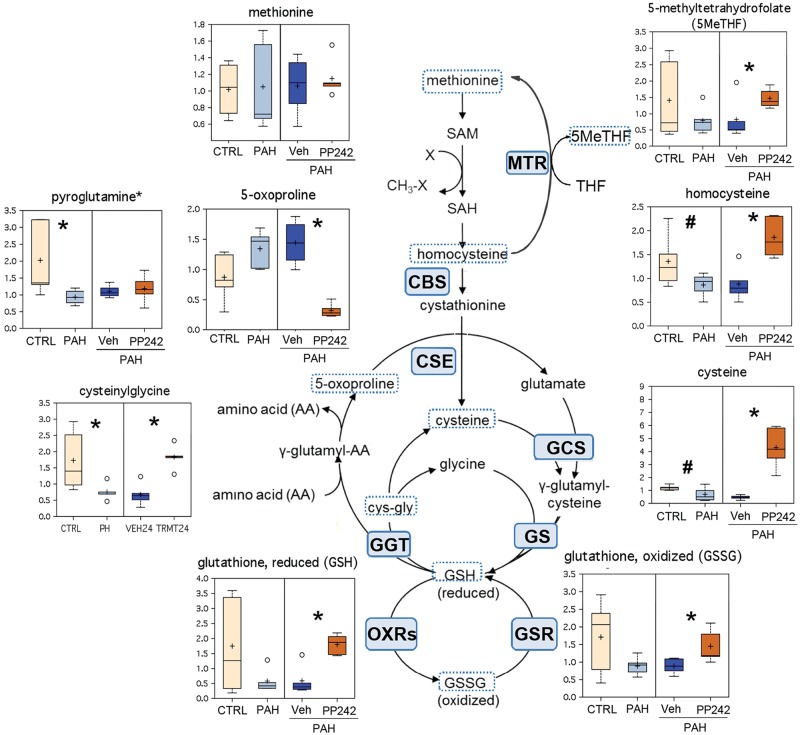
Figure 5.
Components of cysteine metabolism, redox homeostasis, and the γ-glutamyl cycle in control (CTRL), pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) pulmonary arterial vascular smooth muscle cells (PAVSMCs), and PAH PAVSMCs treated with mTOR kinase inhibitor PP242. Box plots for altered metabolites, combined with reaction schemes including key components and enzymes, are shown. Data for PAVSMCs (5 subjects/group) are presented as box-and-whiskers graphs as follows: light yellow: nondiseased (control); light blue PAH PAVSMCs; dark blue: vehicle-treated PAH PAVSMCs (Veh); orange: PP242-treated PAH PAVSMCs (details in Fig. S2). Data are in arbitrary units specific to internal standards for each quantified metabolite and normalized by total protein concentration. *P ≤ 0.05, #0.05 < P < 0.1 by the Welch 2-sample t test. Enzymes that catalyze particular steps in the pathway are shown in blue boxes labeled with their abbreviations according to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes database. CBS: cystathionine-β-synthase; CSE: cystathionine gamma-lyase (cystathionase); GCS: glutamylcysteine synthetase; GGT: gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase 1; GS: glutathione synthetase; GSR: glutathione reductase; MTR: methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase; OXRs: oxidoreductases. cys-gly: cysteinylglycine; GSH: reduced glutathione; GSSG: oxidized glutathione; SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; THF: tetrahydrofolate. mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin.