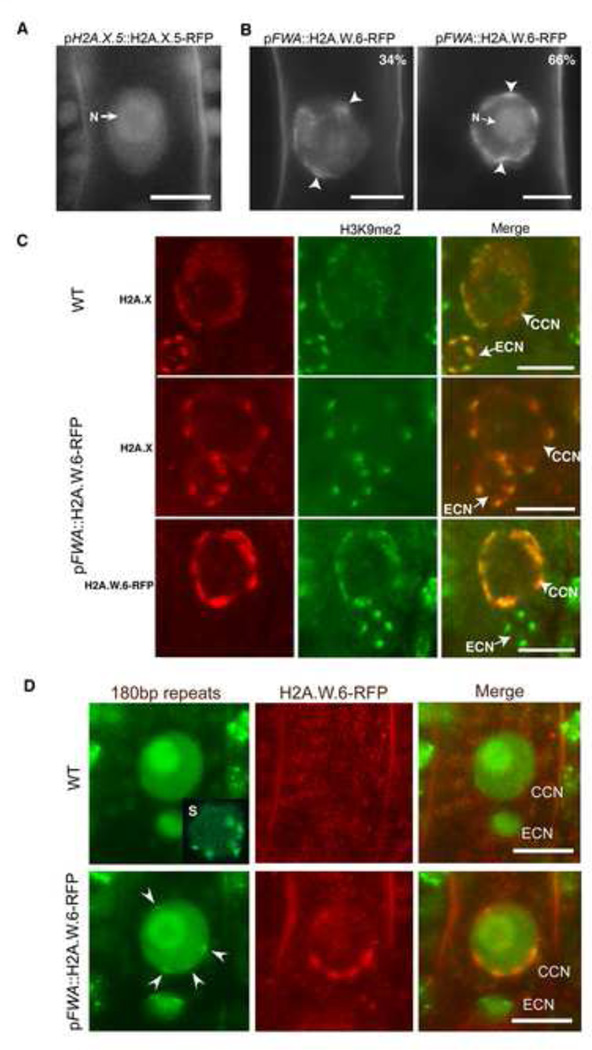
Figure 6. H2A.W is sufficient to cause chromatin condensation in vivo.
(A) Uniform pattern of pH2A.X.5-H2A.X.5-RFP expressed in the central cell nucleus indicating the absence of defined chromocenters. N points the nucleolus. (B) Impact of ectopic expression of H2A.W.6-RFP in the central cell nucleus (CCN). We observe mild or severe chromatin condensation (arrowheads) and the proportion of each type of nuclei is indicated in the top right of each image. N points the nucleolus. (C) Impact of ectopic expression of H2A.W.6-RFP in the CCM on H2A.X and H3K9me2 immunolocalization. Top panel - The egg cell nucleus (ECN) shows well-defined chromocenters reported by H2A.X condensation and marked with H3K9me2 and serve as a reference point for comparison with the cc nucleus. Middle panel – Ectopic expression of H2A.W.6 in the CCN causes condensation of chromatin domains reported by H2A.X. Lower panel – These domains are marked with H3K9me2 (lower panel). (D) A CCN expressing PZFGFP that recognizes the centromeric 180bp repeats. Top panel – In the WT, PZF-GFP marks condensed centromeres in somatic cells (S, insert, a nucleus from root cells) but does not mark any condensed structure in the CCN. Bottom panel – In a central cell expressing pFWA::H2A.W.6-RFP arrowheads point the position of condensed chromatin domains which contain a dot of PZF-GFP marking the centromeric location. Scale bars in confocal sections represent 5 µm. See also Figure S5.