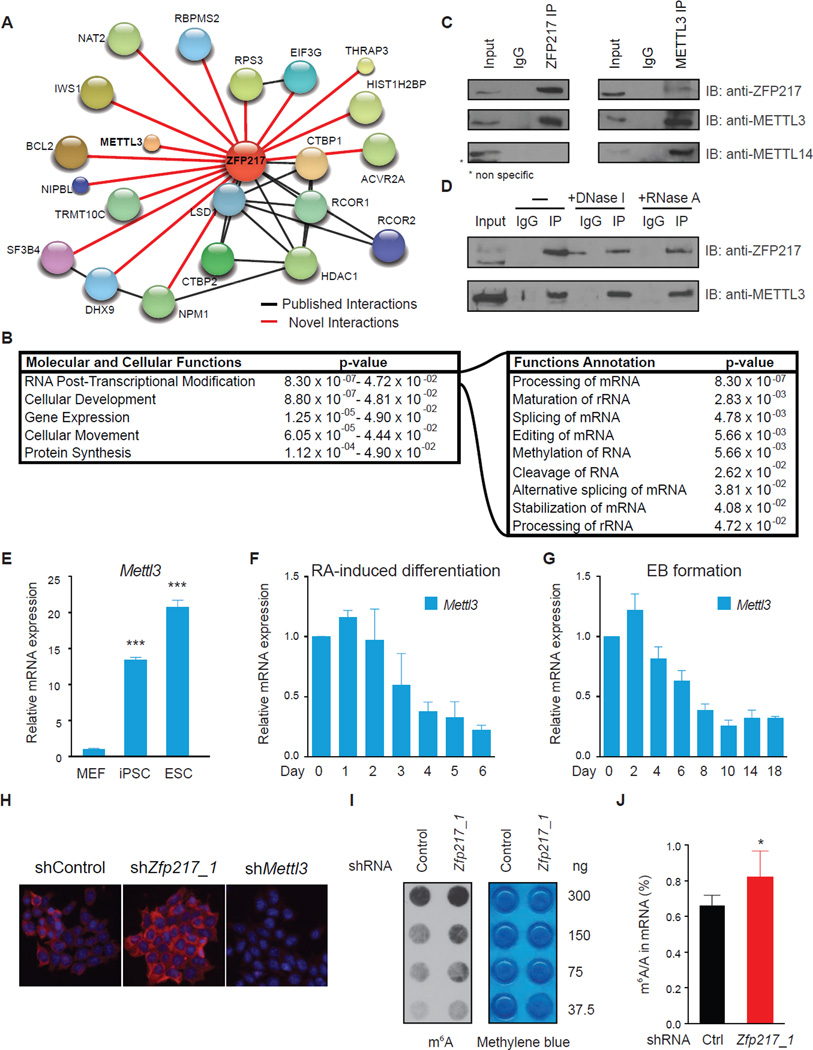
Figure 5. ZFP217 interacts with METTL3 and counteracts its activity.
(A) Diagram depicting the network of associated proteins identified through LC-MS/MS of ZFP217. Black and red lines represent published and novel interactions, respectively.
(B) IPA analysis of proteins identified with LC-MS/MS. Left box describes the molecular and cellular functions. Right box describes function annotations of the RNA post-transcriptional modification category.
(C) Immunoprecipiation of nuclear extracts from ESCs with antibodies against ZFP217 (left panel) or METTL3 (right panel) followed by immunoblotting with ZFP217, METTL3 and METTL14 antibodies. IgG was used as a control.
(D) Immunoprecipiation of nuclear extracts pretreated with DNase I or RNase A with antibodies against ZFP217 followed by immunoblotting with ZFP217 and METTL3 antibodies. IgG was used as a control.
(E) RT-qPCR analysis of Mettl3 expression in MEFs, iPSCs and ESCs. Error bars show ± SD; n = 3. ***p<0.0005 versus MEFs.
(F and G) RT-qPCR analysis of Mettl3 during RA-induced differentiation (F) and EB formation (G). Error bars show ± SD; n = 3
(H) m6A immunostaining of ESCs transduced with control, Zfp217_1, or Mettl3_1 shRNAs. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. The scale bar represents 100 µm
(I) Dot blot analysis of polyadenylated RNA (poly(A)+) isolated from control and Zfp217_1 shRNA ESCs. Indicated amounts were loaded and detected with m6A antibody. Methylene blue staining was used as a loading control.
(J) LC-MS/MS quantification of the m6A/A ratio in polyadenylated RNA isolated from control and Zfp217_1 knockdown ESCs. Error bars show ± SD; n = 2. *p<0.05 versus control shRNA.