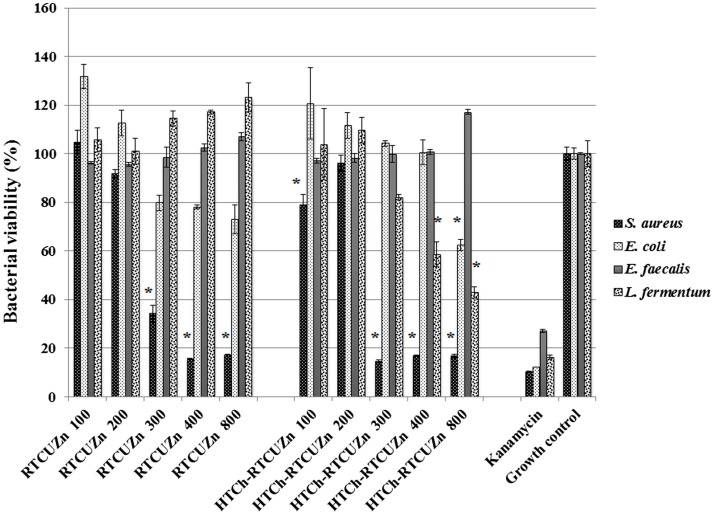
Figure 3.
Microplate alamar blue assay (MABA). Sample name explanation: RTCuZn – mixture of copper sulfate and zinc nitrate in 1% HCl with no HT treatment (no chitosan); HTCh-RTCuZ – copper sulfate and zinc nitrate at room temperature mixed with HT chitosan. HTCh-RTCuZn exhibited superior bacterial killing effect at 800 μg/ml of metallic zinc concentration when screened against all the four model gut bacteria. The numbers in the sample labels represent metallic zinc concentration at 100, 200, 300, 400, and 800 μg/ml. The corresponding chitosan and copper concentrations in those samples are 7.2, 14.4, 21.6, 28.8, and 57.6 μg/ml, respectively. Kanamycin (50 μg/ml) was used as control for bacterial killing. MABA was used as a substitute for broth microdilution assay to screen for effective concentration. The absorbance values of all the test samples were normalized for control samples, i.e., the percentage of viable cells in the growth control is considered as the actual bacterial numbers after 24 h of incubation when there were no antimicrobials added. Higher percentage (than control samples) noticed in some samples corresponds to higher metabolic activity in those samples and the actual number of bacteria is presented in Figure 4. The alamar blue dye undergoes extinction (at a very slow rate) when exposed to light and ambient temperature in the absence of any reducing agent, such as bacteria, and that is observed (~10–20%) in the kanamycin-labeled columns though there were no viable bacteria in there as expressed in Figure 4. [* indicates significant difference between the treatment and respective growth control groups (P < 0.05)].