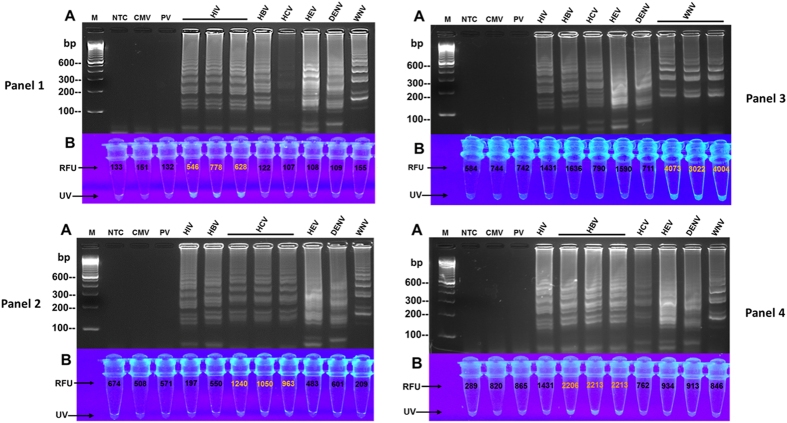
Figure 4. Detection specificity of primers and fluorogenic oligonucleotides.
Ability of the assay to detect specific targets was evaluated utilizing nucleic acid extracts of clinical specimens and multiplex master reaction mixture containing all the primer-sets in Table 1 and only one virus-specific fluorogenic oligonucleotide (LRp) per panel. (A) Electrophoretic results in all 4 panels show detection of the targets as demonstrated by virus-specific ladder-like banding-patterns. No banding pattern was observed in the controls, NTC, CMV, and PV. Distinguishing characteristics of the banding patterns were identified by the grouping/pattern-formation of the bands, size and number of the bands in each pattern, and spacing/distance between the patterns (also see Supplementary Figure S4 for target identification). (B) Intense fluorescence and higher RFU demonstrate that: (i) HIV-LRp specifically hybridized only to HIV RNA in Panel-1; (ii) HCV-LRp specifically hybridized only to HCV RNA in Panel-2; (iii) WNV-LRp specifically hybridized only to WNV RNA in Panel-3; and, (iv) HBV-LRp specifically hybridized only to HBV DNA in Panel-4. M = 100 bp marker; NTC = non-template control; CMV = cytomegalovirus; PV = parvovirus; Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV); Hepatitis-B virus (HBV); Hepatitis-C virus (HCV); Hepatitis-E virus (HEV); Dengue virus (DENV); West Nile virus (WNV); RFU = Relative Fluorescence Units; UV = ultraviolet naked-eye visualization.