Figure 3.
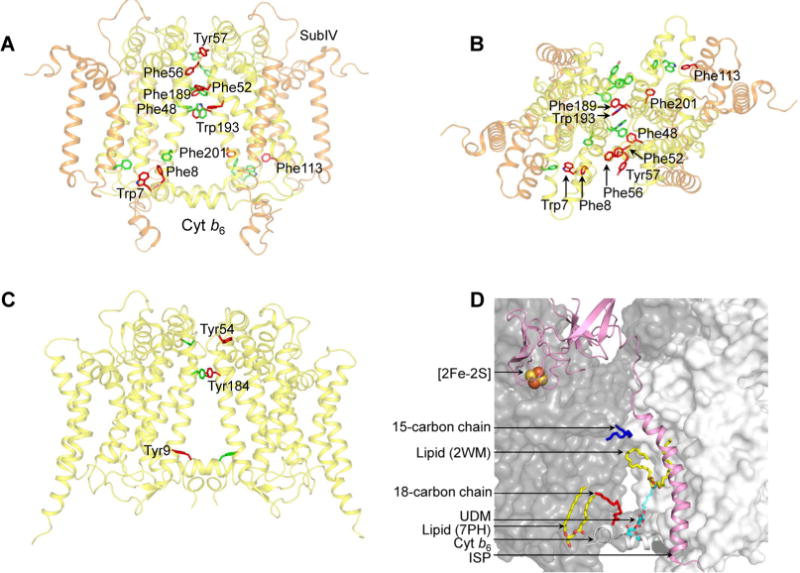
Cyt b6f complex (PDB entry 4OGQ) intermonomer interface. (A) Distribution of transmembrane aromatic residues that contribute to stabilization of the cyt b6f dimer core, which consists of cyt b6 (yellow) and subIV (orange). For the sake of simplicity, only the residues of one monomer (green) are labeled. Residues belonging to the other monomer (red) are not labeled. (B) View of the cyt b6f core along the axis of 2-fold rotational symmetry, normal to the membrane plane. (C) Distribution of transmembrane aromatic residues that contribute to stabilization of the cyt bc1 dimer core (PDB entry 3CX5), which consists of cyt b (yellow). For the sake of simplicity, only the residues of one monomer (green) are labeled. Residues belonging to the other monomer (red) are not labeled. (D) Lipid-mediated stabilization of the cyt b6f complex dimer core. In the 2.5 Å structure of the dimeric complex (PDB entry 4OGQ), four lipidic sites were identified at the intermonomer interface: a 15-carbon chain (dark blue), an 18-carbon chain (red), and two lipid sites (yellow and red). A fifth site, occupied by the detergent UDM (cyan and red), was previously reported in the M. laminosus cyt b6f complex (PDB entry 2E74). The ISP subunit is shown as a pink ribbon. The cyt b6f monomers are shown as white and gray surfaces.
