FIGURE 10.
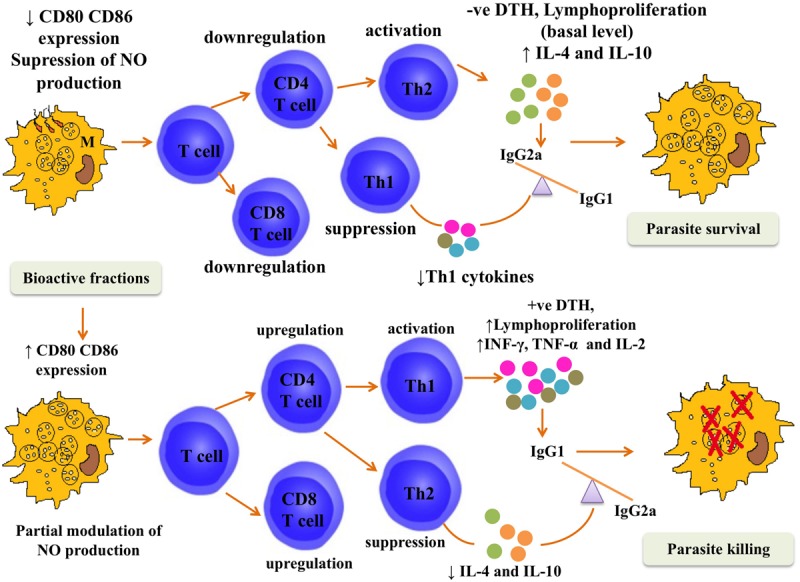
Postulated mechanism for in vivo efficacy of P. nigrum bioactive fractions. The figure depicts that during the course of L. donovani infection in BALB/c mice, the immune response was tilted toward Th2 type. The co-stimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 were downmodulated and NO production was suppressed. CD4+ and CD8+ T cell numbers also declined and the immune response was driven toward Th2 type under the influence of elevated IL-4 and IL-10 levels leading to parasite survival characterized by negative DTH and only basal levels of lymphoproliferation. This immune containment was reversed following treatment with P. nigrum bioactive fractions. The CD80–CD86 expression was elevated, NO was enhanced, and splenic CD4+ and CD8+ T numbers were also augmented. Enhanced secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (INF-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2) further strengthened the Th1 potentiation as was evident from positive DTH and strong lymphoproliferative response and led to parasite killing.
