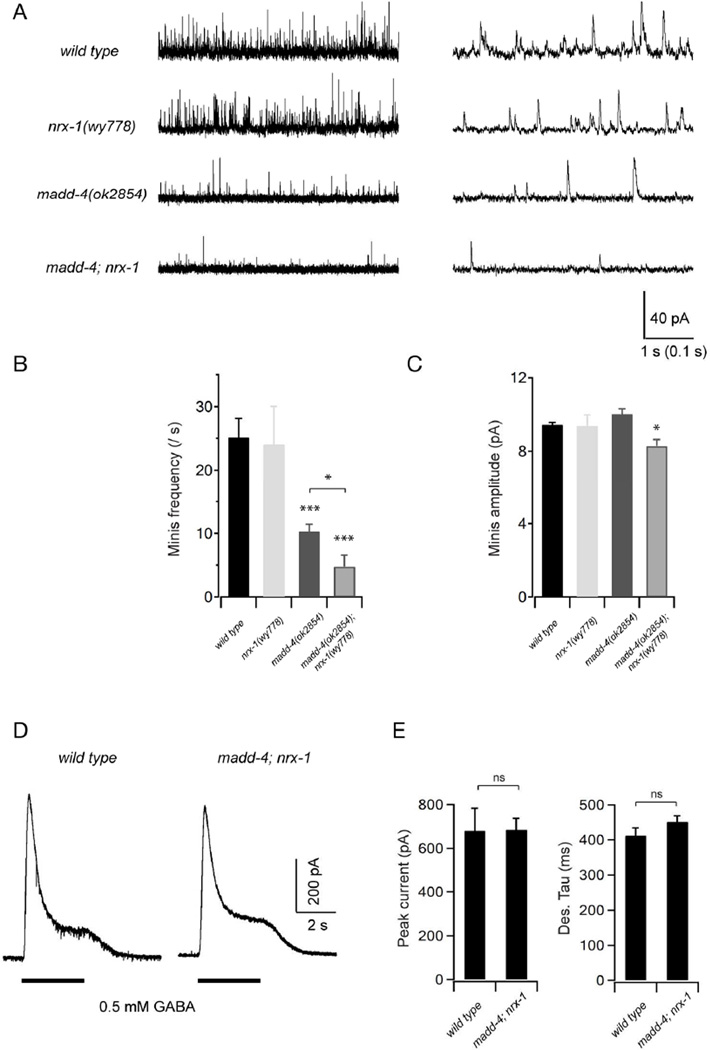
Figure 5. MADD-4 and NRX-1 are redundantly required for GABAergic synaptic transmission.
(A) Representative traces of spontaneous GABAergic mIPSCs in wild-type (WT) animals, as well as nrx-1, madd-4 and madd-4; nrx-1 mutants with different time scales. Body wall muscles were held at −10mV. (B,C) Quantification of the frequency and amplitude of mIPSCs in various genetic backgrounds. Both the mIPSCs frequency and amplitude were significantly decreased in madd-4; nrx-1 double mutants, whereas only mIPSCs frequency was decreased in madd-4 single mutants. Neither mIPSCs frequency nor amplitude was significantly changed in nrx-1 mutants when compared to wild-type animals. (D) Representative traces of GABA (0.5 mM) evoked currents at muscle cells. (E) The peak amplitude and desensitization kinetics of GABA-evoked currents in madd-4; nrx-1 double mutants were comparable to that in wild-type animals. * p<0.05, *** p<0.001, ns: not significant, by the Mann-Whitney U test.