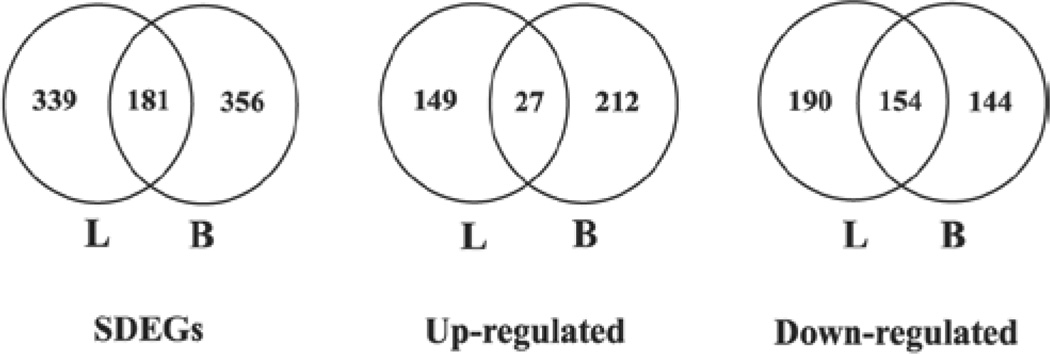
Figure 4.
Number of significantly differentially expressed genes (SDEGs) in the lungs (L) and blood (B) of silica-exposed rats. Rats were exposed to crystalline silica or air and gene expression profile was determined in the lungs and blood by microarray analysis. Genes with >1.5-fold change and a false discovery rate (FDR) p < 0.01 in the silica-exposed rat lungs and blood compared with the corresponding control samples were considered as significantly differentially expressed. SDEGs – Significantly differentially expressed genes in the lungs and blood of the silica-exposed rats compared with the control samples; Upregulated – genes which were significantly overexpressed in the lungs and blood of the silica-exposed rats compared with the control samples; and Downregulated – genes whose expressions were significantly downregulated in the lungs and blood of the silica-exposed rats compared with the control samples.