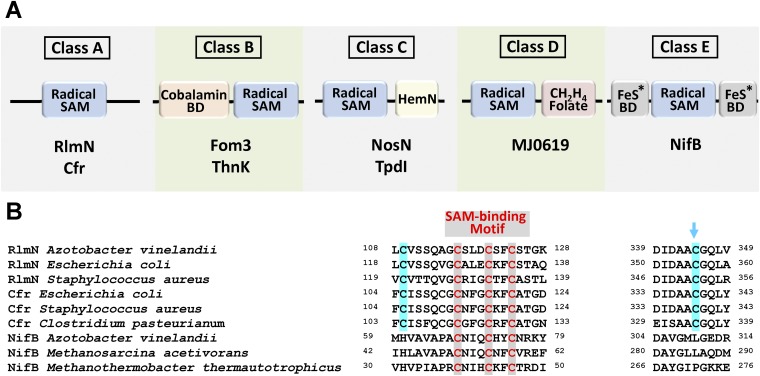
Fig. S5.
(A) Five classes of radical SAM methyltransferases (RSMTs) and (B) partial sequence alignment of members of class A and class E. Class A proteins have a canonical radical SAM domain and two conserved Cys residues that facilitate methyl transfer; class B proteins have a radical SAM domain and an N terminus cobalamin binding domain, and they can use methyl-cobalamin in methylation reactions; class C proteins have a radical SAM domain and a C terminus HemN domain that assists with substrate binding; and class D proteins have a radical SAM domain and a C terminus methylenetetrahydrofolate domain and, unlike proteins of classes A, B, and C, they may use methylenetetrahydrofolate instead of SAM as the source of the methyl carbon (21, 22). Class E proteins have a radical SAM domain and conserved Cys and His residues that serve as FeS cluster-binding domains, and they are presumably specialized in complex metallocluster assembly. BD, binding domain. Representative members of all classes are shown in A. The blue arrow in B indicates the site of intermediary methylation in Rlm and Cfr.