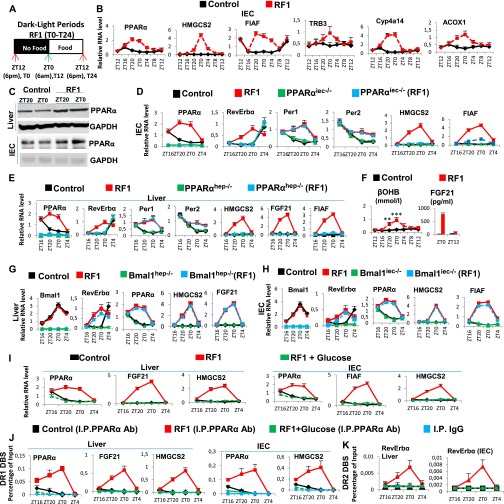
Fig. S2.
Early RF induces temporally aberrant PPARα signaling. (A) A schematic representation of the RF1 experiment. (B) RNA transcript levels of indicated genes in IECs of control and RF1 mice. (C) Immunoblot analyses to evaluate the levels of PPARα in liver and IECs of control and RF1 mice. (D) RNA transcript analysis of genes, as indicated, in IECs of control and RF1 mice with or without an IEC-selective mutation of PPARα (PPARαiec−/−). (E) RNA transcript analysis of genes, as indicated, in liver of control and RF1 mice with or without a liver-selective mutation of PPARα (PPARαhep−/−). (F) Levels of ketone bodies (βOHB) and FGF21 in RF1 blood. (G) RNA transcript analysis of genes, as indicated, in liver of control and RF1 mice with or without a liver selective mutation of Bmal1 (Bmal1hep−/−). (H) RNA transcript analysis of genes, as indicated, in IECs of control and RF1 mice with or without an IEC-selective mutation of Bmal1 (Bmal1iec−/−). (I) RNA transcript levels of indicated genes in liver and IECs of control and RF1 and RF1+Glucose mice. (J) ChIP-qPCR assays in liver and IECs of control, RF1, and RF1+Glucose mice to analyze the PPARα recruitment to the DR1 DBSs present in the indicated genes. (K) As in J, but to analyze the PPARα recruitment to the RevErbα DR2 DBS. All values are mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.