Figure 4.
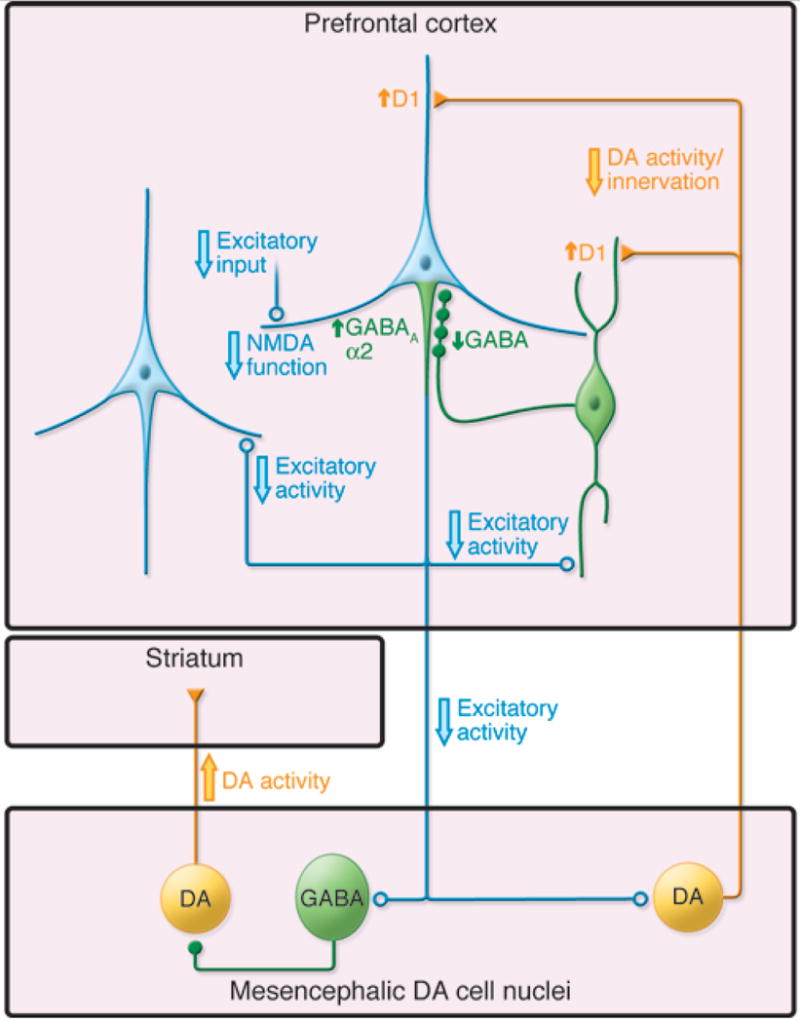
Circuit model of neuronal changes relevant to models of schizophrenia. Excitatory activity of cortical pyramidal neurons (light blue) is thought to be reduced in schizophrenia, most likely due to NMDA receptor hypofunction. Because of interactions with inhibitory, GABAergic interneurons (green), decreased excitatory input to neurons in the mesencephalon would lead to increased dopamine activity in the striatum and decreased dopamine activity in the cortex (yellow). Reprinted by permission from the American Society of Clinical Investigation: Journal of Clinical Investigation [63], copyright 2009.
