Figure 1.
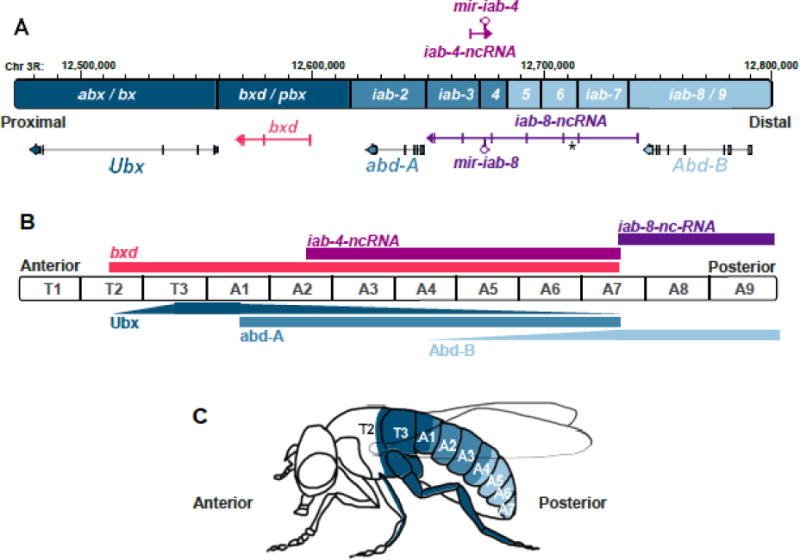
The Drosophila Bithorax complex (BX-C). (A) Physical and genetic organization of the BX-C. The regulatory regions that control the expression of the three Hox protein-coding genes (Ubx, abd-A and Abd-B) are shown in shades of blue and labeled on the schematic of the chromosome. For the infra-abdominal (iab) region, note that iab-4 through iab-6 are abbreviated as 4, 5, and 6. Transcription from the top strand of the BX-C (proximal to distal) is shown above the chromosome in A; transcription of the bottom strand is shown below. All of the transcripts of homeodomain-encoding genes derive from the bottom strand. Non-coding transcripts with cDNA evidence are shown in colored arrows except msa, which is similar to iab-8-ncRNA but differs in the transcription start site (marked with an asterisk). Note that other non-coding transcripts defined by in situ hybridization evidence are not shown in this diagram (see text for details). (B) Schematized domains of expression of the BX-C members along the anterior/posterior axis of an embryonic VNC. The ncRNAs are shown above the diagram, and the protein distributions are shown below. The figure represents a simplified view of the complex pattern of expression within each segment, thus no variations in the compartments are shown. The anterior limit of expression of the bxd transcript shown in the figure corresponds to bxd exon 5 described in Pease et al. (2013), not to the major bxd transcript referred in the same study. (C) Regions of the adult fly specified by each Hox protein-coding gene, inferred by mutations in either the coding region or the regulatory sequences of each transcription unit. No phenotype in the adult morphology has been identified for BX-C ncRNA mutants; however, as discussed in subsequent figures, the miRNAs affect VNC patterning and neural differentiation. T2-A7 stand for thoracic (T) or abdominal (A) segments.
