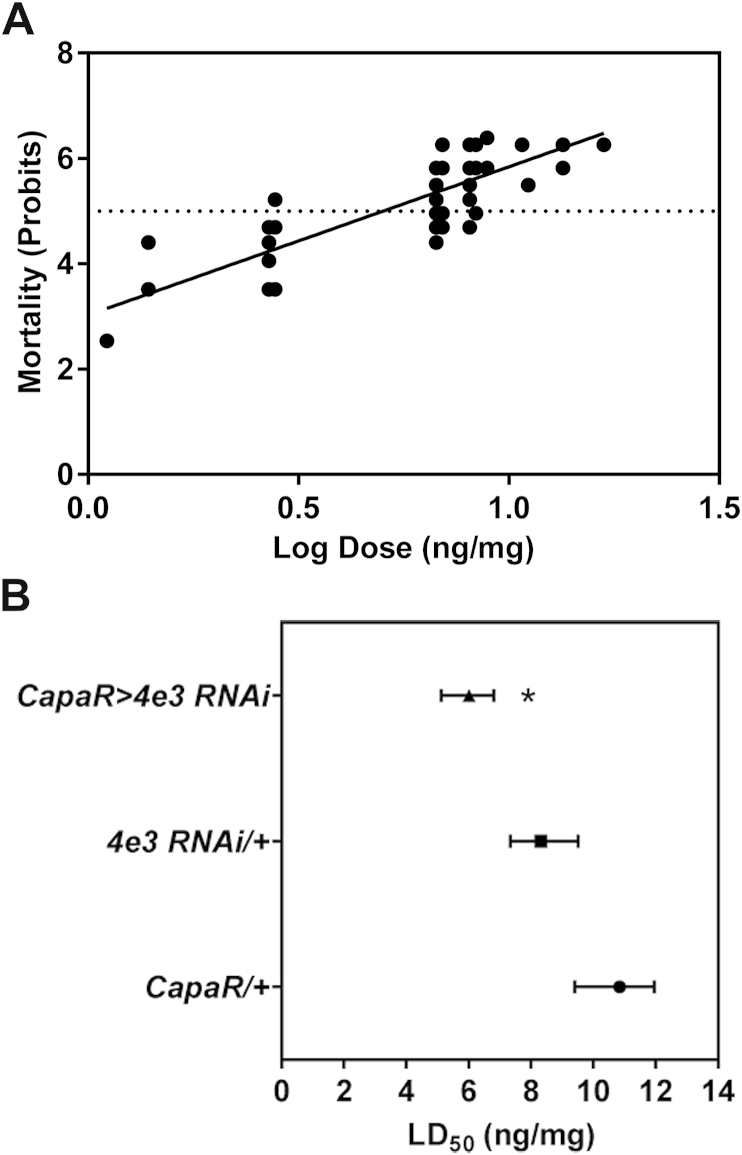
Fig. 3.
PM topical application and the effect on Cyp4e3 knockdown flies. (A) Wild-type Canton-S male flies were exposed to PM, and mortality measured at 24 h. Probits were plotted against the Log of the dose per mg body weight (n = 150 male adult wild-type flies for each concentrations tested). (B) For the different genotypes, a linear regression analysis was performed to determine the dose at which 50% mortality was observed (LD50). Significant change in LD50 was tested using the Litchfield & Wilcoxon method. Knockdown of Cyp4e3 in principal cells of Malpighian tubules significantly reduced the PM LD50 dose compared to both parental controls (*P < 0.001; n > 380 male flies for the different genotypes).