Figure 1. ASC/TMS1 inactivation by promoter hypermethylation in RCC cell lines.
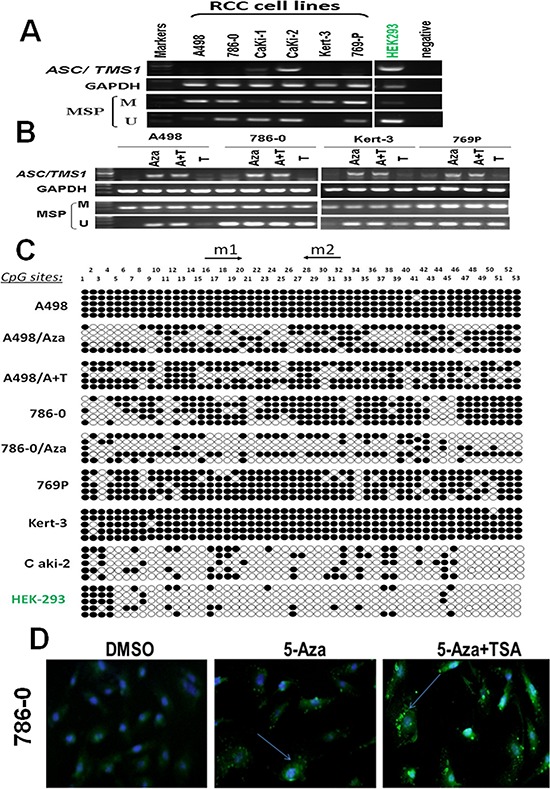
A. ASC/TMS1 was frequently silenced or reduced in RCC cell lines by promoter hypermethylation. HEK293, normal human embryonic kidney cell line. M, methylated. U, unmethylated. B. Pharmalogic demethylation with 5-Aza alone or combined with trichostatin A (A + T) restored ASC/TMS1 mRNA expression and induced its demethyation in RCC cell lines. C. Methylation status of individual CpG sites in the ASC/TMS1 promoter was confirmed by bisulfite genomic sequencing. Each row represents one bacterial clone with one circle symbolizing one CpG site. Filled ovals indicate methylated. Open ovals indicate unmethylated. D. Immunofluorescence staining of ASC/TMS1 protein in 786-O cells. Pharmalogic demethylation with 5-Aza alone or combined with trichostatin A (A + T) restored ASC/TMS1 protein expression in 786-O cells. Green pellet in the cytoplasm and nucleus represents positive staining (indicated by arrows).
