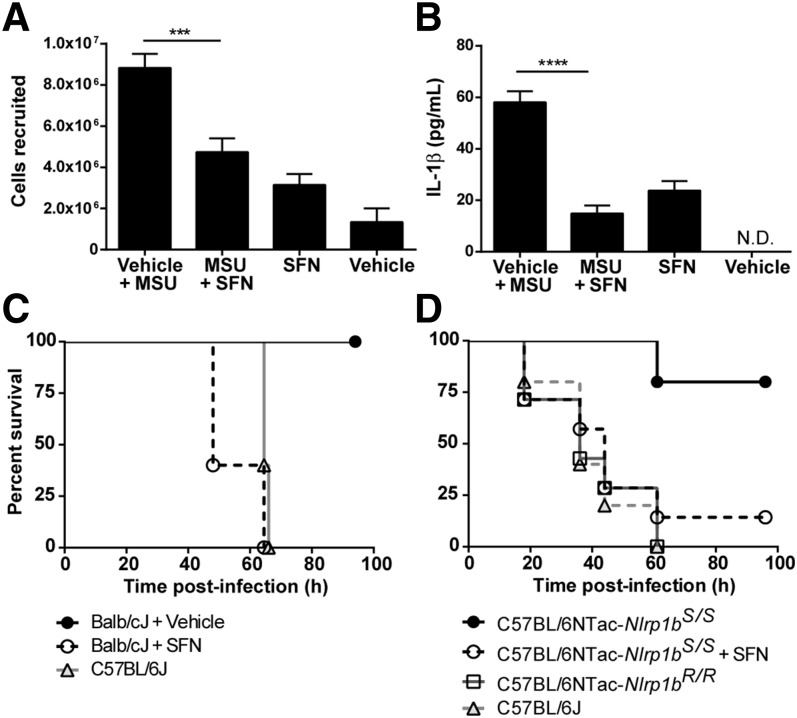
Figure 7. SFN inhibits the inflammasome in vivo.
(A–B) C57BL/6J mice were injected i.p. with 25 mg/kg SFN or the vehicle, followed after 5 min by injection of MSU crystals (i.p.; 4 mg in 250 μl PBS) or the vehicle. After 4 h, mice were again treated with SFN or the vehicle. At 6 h after MSU treatment, a peritoneal lavage was performed and cell recruitment to the peritoneum (A) and IL-1β levels (B) were measured. N.D., not detected. (A–B) Data are pooled means ± sem of 2 independent experiments. Vehicle + MSU, n = 9; MSU + SFN, n = 9; SFN, n = 7; vehicle, n = 4. ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001. The differences seen between SFN-treated and vehicle-treated groups were not significant (P = 0.067). (C) B. anthracis-resistant Balb/cJ mice (n = 5/group) were injected with 32 mg/kg SFN or the vehicle (i.p.) at 2 h before infection and subcutaneously at the time of challenge at a site distal to spores. All mice were challenged with 2 × 107 spores (s.c.). Anthrax-susceptible C57BL/6J mice (n = 5) were challenged as controls. (D) B. anthracis-resistant C57BL/6JNTac-Nlrp1bS/S mice were injected with 30 mg/kg SFN or vehicle (i.p.) at 2 h before the infection, and s.c. at the time of the challenge at a site distal to the spores. All mice were challenged with 5 × 107 spores (s.c.). Anthrax-susceptible C57BL/6J and C57BL/6JNTac-Nlrp1bR/R mice were challenged as controls. C57BL/6NTac-Nlrp1bS/S + vehicle, n = 5; C57BL/6NTac-Nlrp1bS/S + SFN, n = 7; C57BL/6NTac-Nlrp1bR/R + vehicle, n = 7; C57BL/6 + vehicle, n = 5.