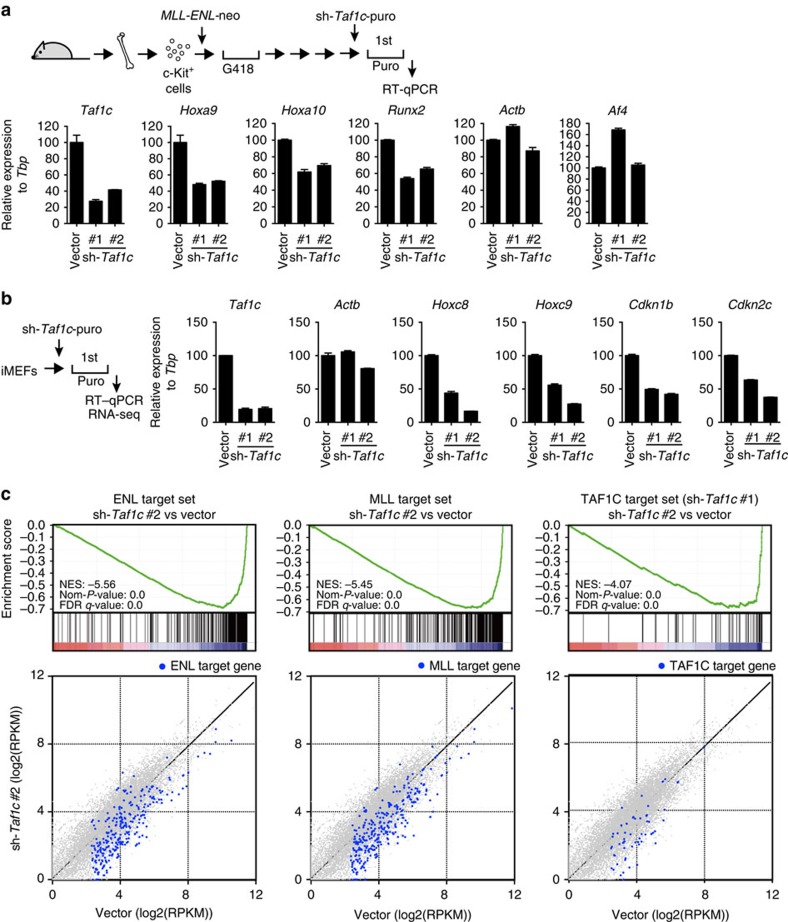
Figure 4. TAF1C is required for gene activation by MLL–ENL and AEP.
(a) The expression of MLL–ENL target genes (Hoxa9, Hoxa10 and Runx2) after knockdown of Taf1c with two different shRNAs in MLL–ENL-transformed cells. The expression level normalized to Tbp is shown relative to the value of the vector control (arbitrarily set at 100%) with error bars (s.d. of PCR triplicates). Puro, puromycin. (b) Effect of Taf1c knockdown on AEP-dependent gene activation. Taf1c was knocked down with two different shRNAs in iMEFs. The expression of AEP target genes (Hoxc8, Hoxc9, Cdkn1b and Cdkn2c) was analysed with reverse transcriptase (RT)–qPCR as described in a. (c) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the expression profiles of iMEFs after knockdown of Taf1c (#1 and #2), Enl and Mll. Genes that exhibited a greater than threefold decrease on knockdown in RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) were defined as target genes (Supplementary Fig. 3c,d). The target gene sets of ENL, MLL and TAF1C (shRNA#1) were downregulated by knockdown of Taf1c with shRNA#2. Expression levels of the target genes were also shown by scatter plots. Target genes of ENL, MLL and TAF1C are highlighted in blue. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score; Nom-P-value, nominal P-value; RPKM, reads per kilobase of exon per million mapped reads.