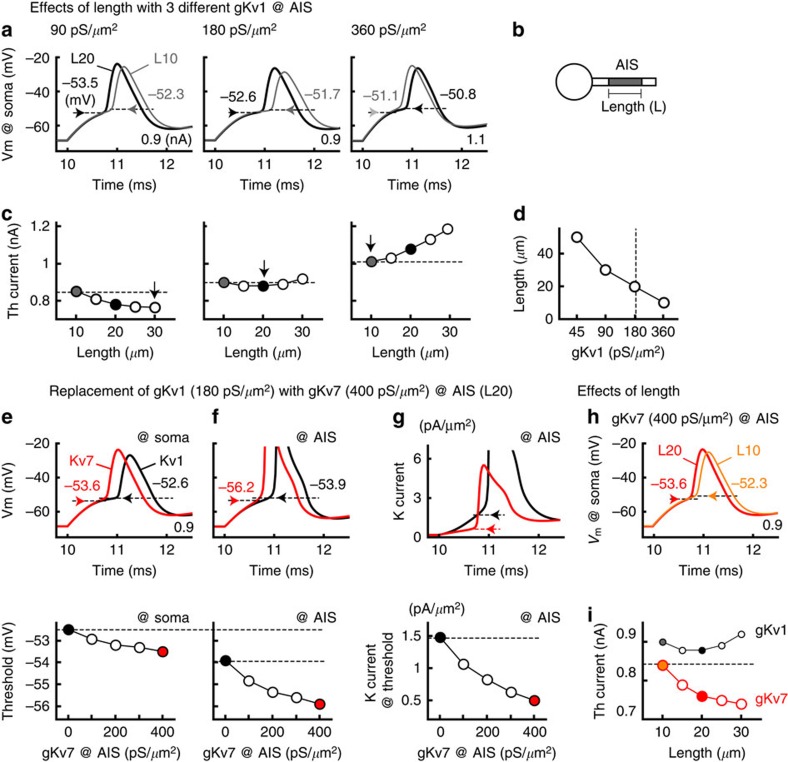
Figure 6. Replacement of Kv1 with Kv7 at the AIS increased excitability in a model neuron.
(a) Effects of AIS length on APs in three different Kv1 conductances (gKv1) at the AIS. The APs from AIS length (L) of 10 μm (L10, grey) and 20 μm (L20, black) were overlaid; 90 pS μm−2 (left), 180 pS μm−2 (middle) and 360 pS μm−2 (right). Horizontal arrows indicate the AP threshold. A somatic current injection (20 ms) was made to induce APs; the amplitude is specified on the lower right. (b) Schematic drawing of model neuron (Methods). (c) Relationship between threshold current and AIS length. Note that the AIS length affected the threshold current differentially depending on gKv1 at the AIS. Vertical arrows indicate the minimum threshold current. (d) AIS length that provides a minimum threshold current negatively correlated with gKv1. (e–g) Effects of replacing gKv1 (180 pS μm−2, black) with gKv7 (400 pS μm−2, red) at the AIS. The gKv1 and gKv7 were changed to make total K+ current constant at the rest (Methods). The top panels show the APs at the soma (e) and at the AIS (f) and the K+ current at the AIS (g). The threshold (e,f) and K+ current at threshold (g) are indicated by horizontal arrows and are plotted against ratio of gKv7 (bottom). Note that the replacement lowered the threshold at both the soma and the AIS and reduced the K+ current at threshold at the AIS. (h) Effects of AIS length on APs in a model with gKv7 (400 pS μm−2) at the AIS. The APs from the AIS length of 10 μm (L10, orange) and 20 μm (L20, red) are overlaid. (i) The threshold current decreased monotonically with the AIS length in the model with gKv7 (400 pS μm−2, red), and it was systematically smaller than that in the model with gKv1 (180 pS μm−2, black, from c middle). The replacement of gKv1 with an equal density of gKv7 (180 pS μm−2) further augmented the reduction of the threshold current. It is important to note that replacement or reduction of gKv1 at the AIS did not affect input resistance of the soma.