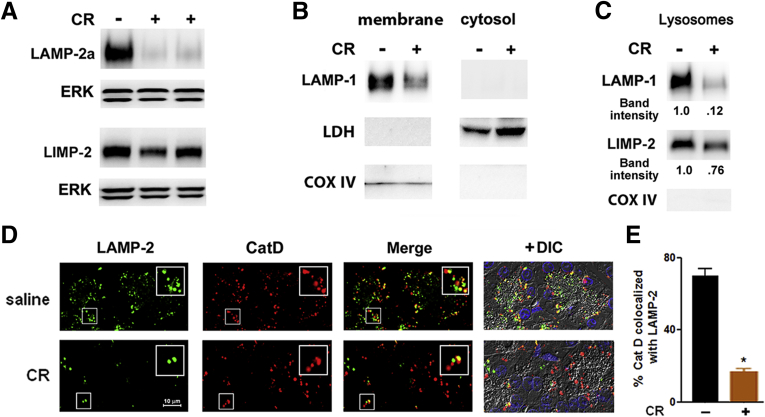
Figure 2.
Experimental pancreatitis causes a decrease in lysosome-associated membrane proteins (LAMPs), including LAMP-2a, but not in lysosomal integral membrane protein type-2 (LIMP-2). Cerulein (CR) pancreatitis was induced in mice (A–C) and rats (D). Pancreatic levels of indicated proteins were measured by immunoblot, using C-terminal Abs, in (A) whole tissue homogenates, (B) membrane and cytosolic fractions, and (C) lysosome-enriched fraction (see Materials and Methods). Extracellular signal-activated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2), lactate dehydrogenase, and cyclooxygenase IV (COX IV) served as controls for equal loading and the quality of subcellular fractionation. Data in B and C are representative of two independent experiments, with similar results. (D) Colocalization of LAMP-2 and cathepsin D (CatD) in pancreas of control (saline) rats and rats with CR pancreatitis. Tissue sections were double immunostained for LAMP-2 (using C-terminal Ab) and CatD. Insets show higher magnification for the areas in smaller boxes. Scale bar is the same for all images. DIC, differential interference contrast. (E). CatD colocalization with LAMP-2 was quantified with ImageJ. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 3–4 per group); *P < .05 versus control.