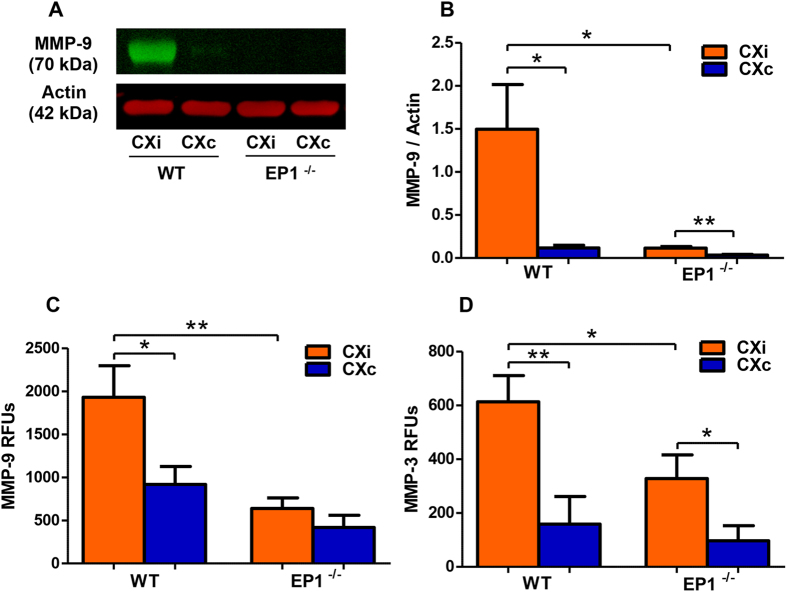
Figure 10. EP1−/− mice show reduced MMP-9 protein levels and MMP-9/-3 activity.
MMP-9/-3 protein levels were measured by immunoblotting, and enzymatic activity was quantified to determine if EP1−/− mice show reductions consistent with the rat data. (A) A representative immunoblot of MMP-9 in the mouse cortex. (B) Densitometric analysis shows that MMP-9 is elevated in the ischemic hemisphere of both groups compared to the contralateral hemisphere (P < 0.05, P < 0.01 unpaired two-tailed t-test). EP1−/− mice have dramatically reduced MMP-9 protein levels in the ischemic cortex compared to the wild-type (P < 0.05, unpaired two-tailed t-test). (C) A FRET peptide immunoassay was used to measure MMP-9 activity in the mouse cortex. MMP-9 activity was increased in the ischemic cortex of the WT group compared to the contralateral hemisphere (P < 0.05, unpaired two-tailed t-test), but not in the EP1−/− group (P = 0.26, unpaired-two tailed t-test). MMP-9 activity was reduced in the ischemic cortex of EP1−/− mice compared to the wild-type (P < 0.01, unpaired two-tailed t-test). (D) MMP-3 enzymatic activity was measured using a FRET peptide immunocapture assay. MMP-3 activity was increased in the ischemic cortex compared to the contralateral hemisphere in both groups (P < 0.01, P < 0.05, unpaired two-tailed t-test). MMP-3 activity was reduced in the ischemic cortex of EP1−/− mice compared to the wild-type (P < 0.05, unpaired two-tailed t-test). WT, N = 8; EP1−/−, N = 8. CXi = Cortex ipsilateral to stroke, CXc = Cortex contralateral to stroke.