Fig. 1.
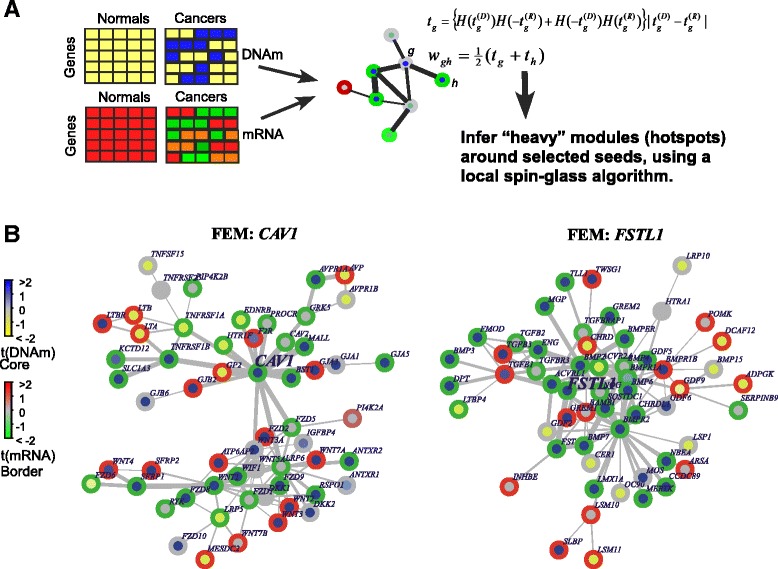
The FEM algorithm and examples of FEM modules in ER+ breast cancer. a The FEM algorithm first uses gene-centred statistics of differential DNA methylation, t (D)g and differential mRNA expression, t (R)g, here between normal and ER+ breast cancer, to weight the edges in a PPI network. The weight of the edge between gene g and h is constructed as indicated, where H(x) denotes the Heaviside function (H(x) = 1 if x > 0, H(x) = 0 if x < 0), which are being used to impose an anti-correlation. Hotspots of differential DNAm and mRNA expression are then inferred by running a module detection algorithm on the PPI network, which attempts to find subnetworks that maximize the modularity (average weight density) locally. b Examples of two FEMs centred around seed genes CAV1 and FSTL1 in ER+ breast cancer
