Fig. 6.
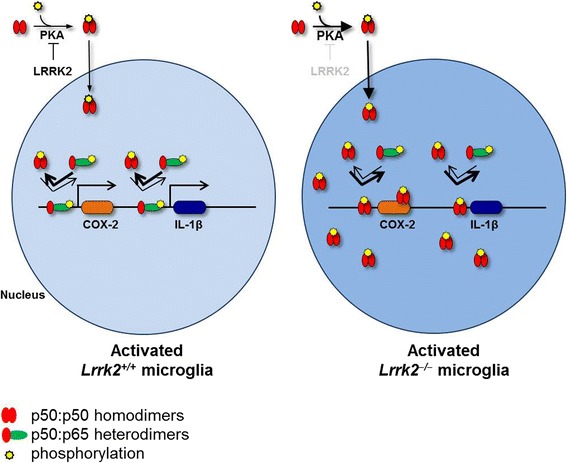
Schematic hypothesis. Genetic deletion of Lrrk2 or inhibition of its kinase activity results in increased phosphorylation of NF-κB inhibitory subunit p50 at S337 with consequent accumulation of p50 in the nucleus. This abnormally higher proportion of nuclear P-p50 might hamper p65:p50 to efficiently bind to DNA and activate genes transcription upon LPS or α-syn-mediated inflammation
